Figure 5.
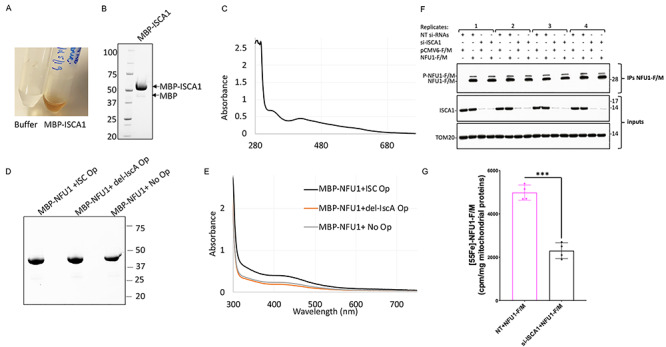
Human ISCA1 ligates a [2Fe–2S] cluster and is required for cluster formation on NFU1. (A) The as-purified MBP-ISCA1 protein from E. coli co-expressing the ISC operon from A. vinelandii eluted as a brown colored solution from the amylose resin. (B) SDS-PAGE separation of purified MBP-ISCA1 protein on a stain-free denaturing gel. (C) UV–visible spectrum of as-purified MBP-ISCA1 shows the characteristic features of a [2Fe–2S] cluster (43). (D) SDS-PAGE separation and (E) UV–visible spectrum of MBP-NFU1 purified from E. coli co-expressing either WT ISC operon (ISC Op), ISC operon with deleted IscA (del-IscA Op) or no operon (No Op) on a stain-free denaturing gel. The MBP-tagged proteins were purified using amylose resin affinity purification followed by the HiTrap Q column ion-exchange purification. (F) IBs on samples as those analyzed in (G) for the 55Fe incorporation into NFU1-F/M showed effective knockdown of ISCA1 in mammalian cells transfected with siRNAs targeting the ISCA1 mRNA and efficient immunoprecipitation of recombinant NFU1-F/M. TOM20 was used as a loading control (G) 55Fe incorporation into NFU1-F/M assessed by liquid scintillation counting showed significantly decreased levels of radioactive iron incorporated into NFU1-F/M upon KD of ISCA1. The background, corresponding to 55Fe measurements of eluates after anti-FLAG immunoprecipitations on mitochondrial extracts from cells transfected with the empty vector, was subtracted from each reading. Unpaired t-test analyses of 55Fe labeling experiments were performed with GraphPad Prism 7. ***P < 0.001.
