Figure 10.
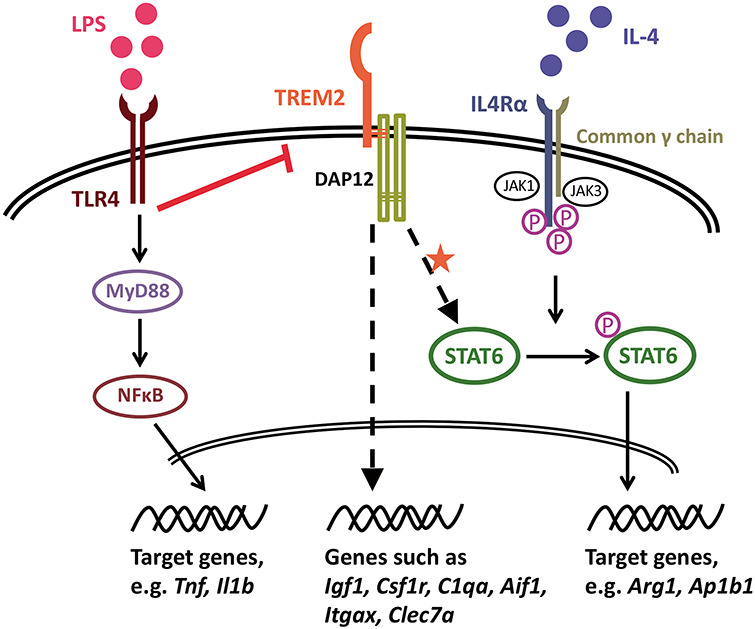
Proposed model of the involvement of TREM2 in the IL-4-induced anti-inflammatory response. LPS induces pro-inflammatory activation of microglia, which is accompanied by down-regulated Trem2 expression, and so microglia with reduced TREM2 activity generally show normal activation in response to the pro-inflammatory LPS stimulus. Under non-stimulated conditions, a number of microglial genes are down-regulated when TREM2 activity is decreased, such as Csf1r expression, which may result in the seen reduced survival of microglia. However, IL-4 induces an anti-inflammatory phenotype of microglia. As our data suggest, TREM2 signaling is involved in maintenance of microglial STAT6 levels, which in the IL-4 pathway is phosphorylated and translocates to the nucleus and functions as a key transcription factor for IL-4-induced gene expression changes, such as for Arg1 and Ap1b1. Thus, Trem2 deficiency results in decreased STAT6 levels in microglia, which leads to an impairment of IL-4-induced signaling. TREM2 also regulates the levels of a number of genes that are up-regulated by IL-4 (suppressed by LPS), and considered a component of the transcriptional response to AD-associated pathology, such as Igf1, C1qa, Itgax and Clec7a.
