Figure 4.
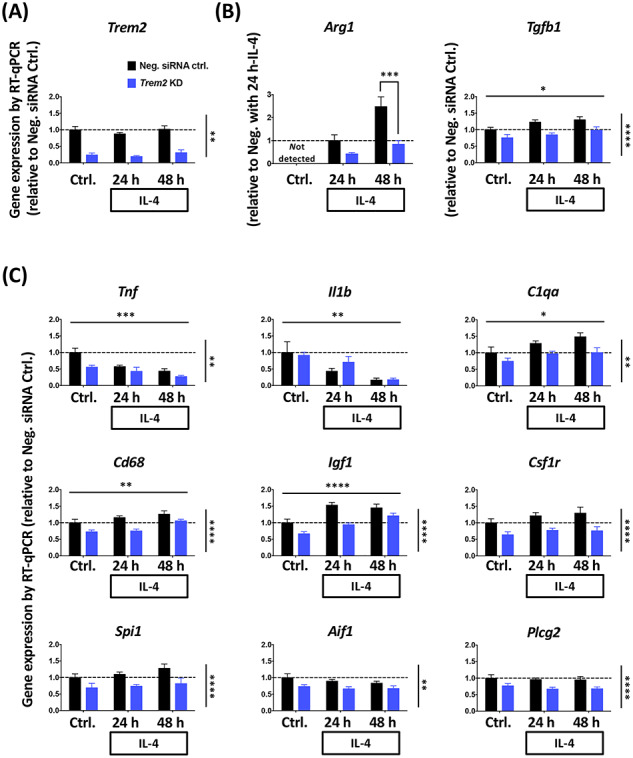
Trem2 knockdown impairs the IL-4-induced anti-inflammatory response of primary microglia. (A) Trem2 gene expression was not significantly influenced by IL-4 stimulation. (B) Arg1 and Tgfb1 expression, as markers of the anti-inflammatory response, showed significant up-regulation with time after IL-4 application. Particularly, Trem2 knockdown greatly decreased IL-4-induced Arg1 expression compared with negative controls. Gene expression levels were normalized to Rps28 and calculated as fold change relative to the negative control without IL-4 treatment in each individual culture preparation, except for Arg1. Two-way ANOVA with significant main effect of IL-4 incubation time and Trem2 knockdown indicated as horizontal and vertical lines respectively. A significant interaction between IL-4 treatment length and Trem2 knockdown was seen only in Arg1 expression (B), and so Sidak’s post hoc tests were performed to test pairwise significance between the negative siRNA control and Trem2 knockdown at each time-point. (C) Expression of the pro-inflammatory genes (Tnf and Il1b) and other microglial genes. Gene expression levels were normalized to Rps28 and calculated as fold change relative to the negative control without IL-4 treatment in each individual culture preparation. N = 7–9 independent experiments. Data shown as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA; significant main effects of IL-4 treatment time and Trem2-knockdown indicated by horizontal and vertical lines respectively, no significant interactions were seen between IL-4 treatment and Trem2 knockdown; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
