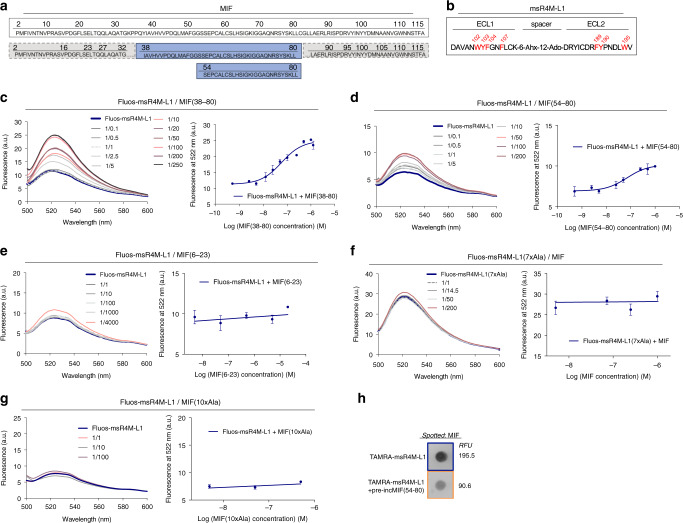
Fig. 2. Mapping of the MIF/msR4M-L1 core binding region and complex disruption by mutations.
a Amino acid sequence of human MIF (boxed, top). The msR4M-L1 binding core region of MIF (sequence 38–80 and 54–80) is indicated in blue, while non-binding stretches are in gray (bottom). b Sequence of msR4M-L1. Aromatic residues identified by peptide array to be critical for MIF binding are highlighted in red. c–e Nanomolar affinity binding of msR4M-L1 to MIF(38–80) (c) and MIF(54–80) (d), but not MIF(6–23) (e), as determined by fluorescence spectroscopy. Emission spectra of Fluos-msR4M-L1 alone (blue; 5 nM) and with increasing concentrations of MIF(38–80) (c), MIF(54–80) (d), and MIF(6–23) (e) (left panels; representative titrations); binding curves derived from the fluorescence emission at 522 nm (right panels). f–g Binding of msR4M-L1 to MIF is blunted when aromatic residues in msR4M-L1 are substituted by Ala in analog msR4M-L1(7xAla) (f) or when N-loop residues in MIF are mutated to Ala in MIF(10xAla) (g). Fluorescence spectroscopy and binding curve as in c–e. Data in right panels of c–g are means ± SD from three independent experiments. h Dot blot shows that binding of TAMRA-msR4M-L1 to spotted MIF is attenuated by MIF(54–80). 400 ng spotted MIF was probed with TAMRA-msR4M-L1 +/− 2-fold molar excess of MIF(54–80); RFU, relative fluorescent units. The blot shown is one of three dot blots performed. msR4M-L1, MIF-specific CXCR4 mimic-L1; MIF, macrophage migration-inhibitory factor. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.