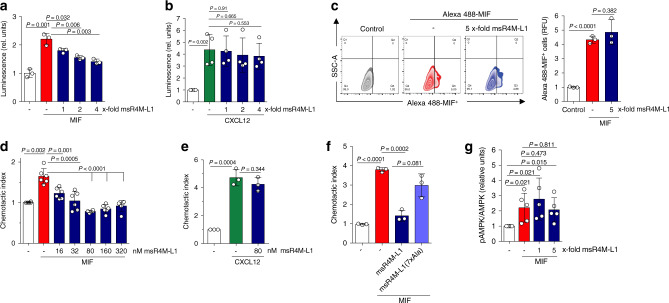
Fig. 3. msR4M-L1 selectively inhibits MIF-triggered CXCR4 activity, but spares the MIF/CD74 axis.
a, b MIF (a) but not CXCL12 (b) binding to and signaling through human CXCR4 in an S. cerevisiae system is attenuated by msR4M-L1 in a concentration-dependent manner. The molar excess of competing msR4M-L1 over MIF or CXCL12 is indicated. CXCR4 binding/signaling is read out by LacZ reporter-driven luminescence. c A 5-fold molar excess of msR4M-L1 does not interfere with binding of Alexa 488-MIF to CD74 expressed on HEK293-CD74 transfectants as measured by flow cytometry. Left, shift of CD74 transfectants following Alexa 488-MIF binding (control indicates background); right, quantification of three independent experiments. d, e Chemotactic migration (Transwell) of primary mouse spleen B lymphocytes elicited by 16 nM MIF (d) or CXCL12 (e) as chemoattractant and inhibitory effect of msR4M-L1. msR4M-L1 dose-dependently inhibits MIF-mediated chemotaxis (d), but the optimal inhibitory dose of 80 nM does not affect CXCL12-elicited chemotaxis (e). f msR4M-L1 analog msR4M-L1(7xAla) does not inhibit MIF-mediated chemotaxis. msR4M-L1(7xAla) was applied at a concentration of 80 nM. g msR4M-L1 does not interfere with MIF-triggered AMPK signaling in the human cardiomyocyte cell line HCM. MIF was applied at a concentration of 16 nM; msR4M-L1 added at 1- and 5-fold excess over MIF. AMPK signaling was measured using Western blot of HCM lysates developed against pAMPK and total AMPK. The densitometric ratio of pAMPK/AMPK indicates signaling intensity. Data are reported as means ± SD of n = 3 (a); n = 4 (b); n = 3 (c, right panel); n = 6 (d); n = 3 (e–f); and n = 5 (g) independent biological experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with unpaired two-tailed T-test. CXCR4, CXC motif chemokine receptor-4; msR4M-L1, MIF-specific CXCR4 mimic-L1; MIF, macrophage migration-inhibitory factor. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.