Table 1.
Antimicrobial resistant bacteria with cost implications in human health or in animal health and production
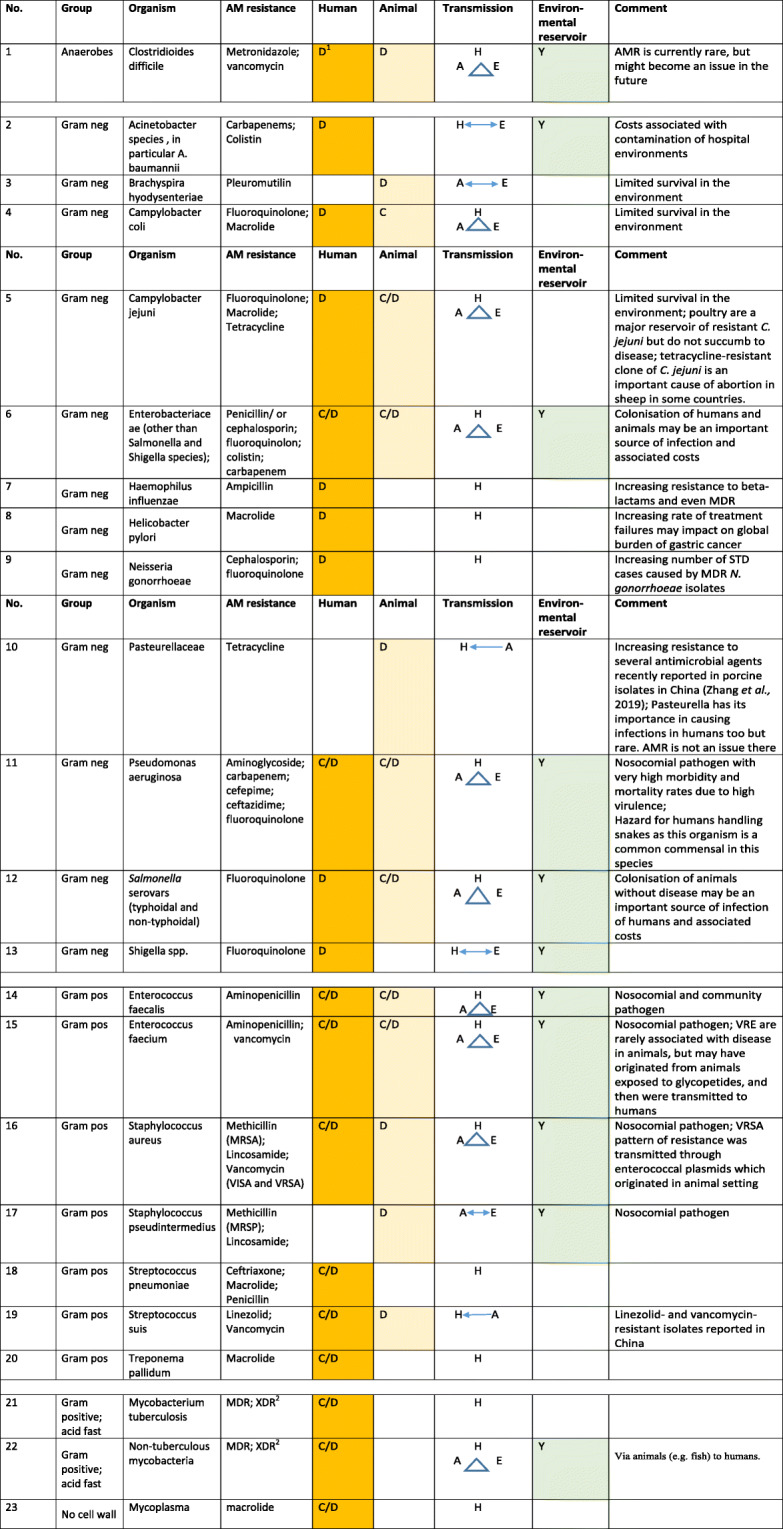
Important routes of transmission and the role of the environment as a reservoir of infection are indicated
1D = disease occurs due to the organism(s), C = no disease but costs associated with colonisation; H = human, A = animal, E = environment, Y = yes
2In the context of mycobacterial infection, MDR is defined as resistance to at least isoniazid and rifampin and XDR as resistance to isoniazid and rifampin and at least 3 of the 6 classes of aminoglycosides, polypeptides, fluoroquinolones, thioamides, cycloserine, and para-aminosalicyclic acid
