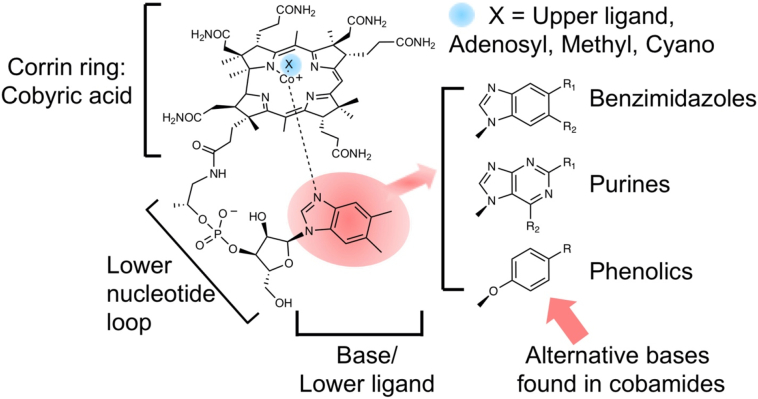
Fig. 1.
Structure of cobalamin (vitamin B12).
The core component of cobalamin is the corrin ring, which houses a central cobalt ion. The corrin ring together with the cobalt is called cobyric acid. Attached to the propionic side chain of cobyric acid is a lower nucleotide loop, that contains an unusual base called dimethylbenzimidazole and which acts as a lower ligand to the cobalt ion. The upper ligand in vitamin B12, marked as a X in the diagram is a cyano group. In the biological forms of cobalamin, the upper ligand is usually a methyl or an adenosyl group. Some bacteria make variant forms of cobalamin where the dimethylbenzimidazole base is replaced with other bases such as other benzimidazoles (with variations around R1 and R2), purines (with variations around R1 and R2) and phenolics (with variations around R).