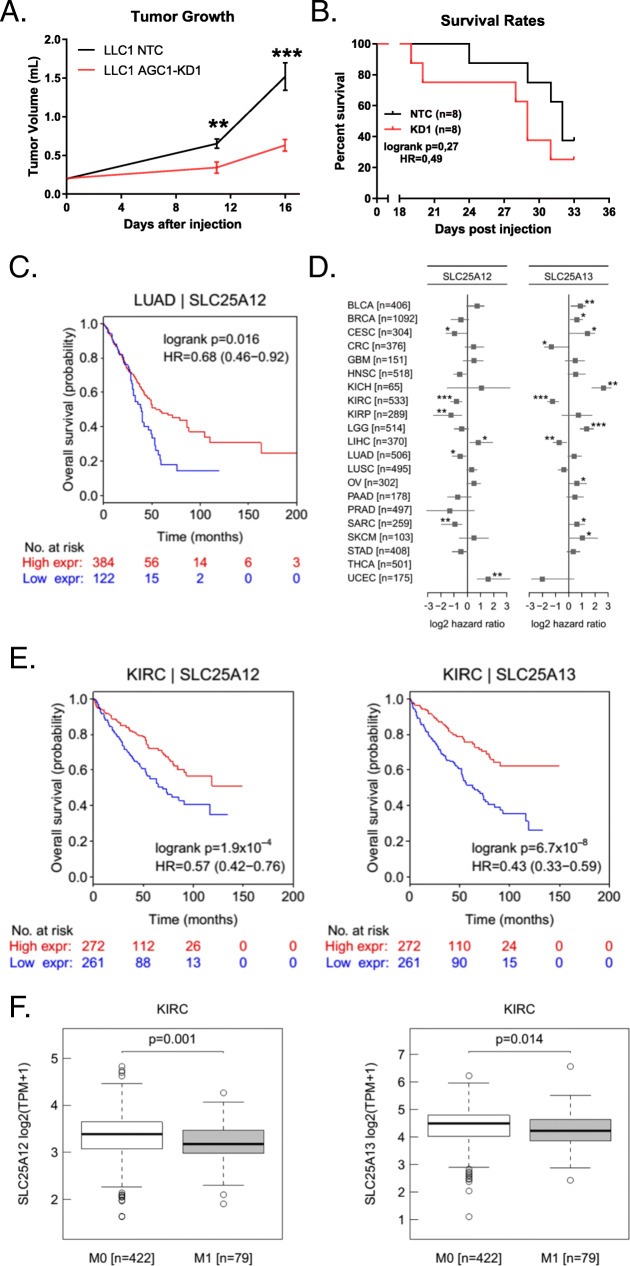
Fig. 1.
AGC1-deficient tumors tend to be more lethal for mice. a Tumor progression of control (NTC) and AGC1-KD LLC1 tumors measured as described above. b Survival rates of the mice bearing control (NTC) and AGC1-KD LLC1 tumors monitored over the course of 33 days. c Overall survival rates of patients with high (red line) or low (blue line) AGC1 (SLC25A12) mRNA-expressing lung adenocarcinomas (LUAD). Data is adopted from the TCGA database. Patients with higher or lower AGC1 (SLC25A12) mRNA expression were divided into two groups with a cutoff line where the separation of these groups was significantly most meaningful. d Correlation of AGC1 (SLC25A12) or AGC2 (SLC25A13) mRNA expression with better (negative log2 hazard ratio) or poor (positive log2 hazard ratio) survival of patients from various cancers. Lower log2 hazard ratio for a gene means that the group of patients with low expressing tumors have worse overall survival than the high-expressing group. The cutoff to separate groups was determined as described in c. e Overall survival (OS) rates of patients with high (red line) or low (blue line) AGC1 (SLC25A12) or AGC2 (SLC25A13) mRNA-expressing kidney renal clear cell carcinoma tumors (KIRC). Data is adopted from the TCGA database. The cutoff to separate groups was determined as described in c. f mRNA expressions of AGC1 (SLC25A12) or AGC2 (SLC25A13) in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma tumors (KIRC) of patients without (M0) or with metastasis (M1)