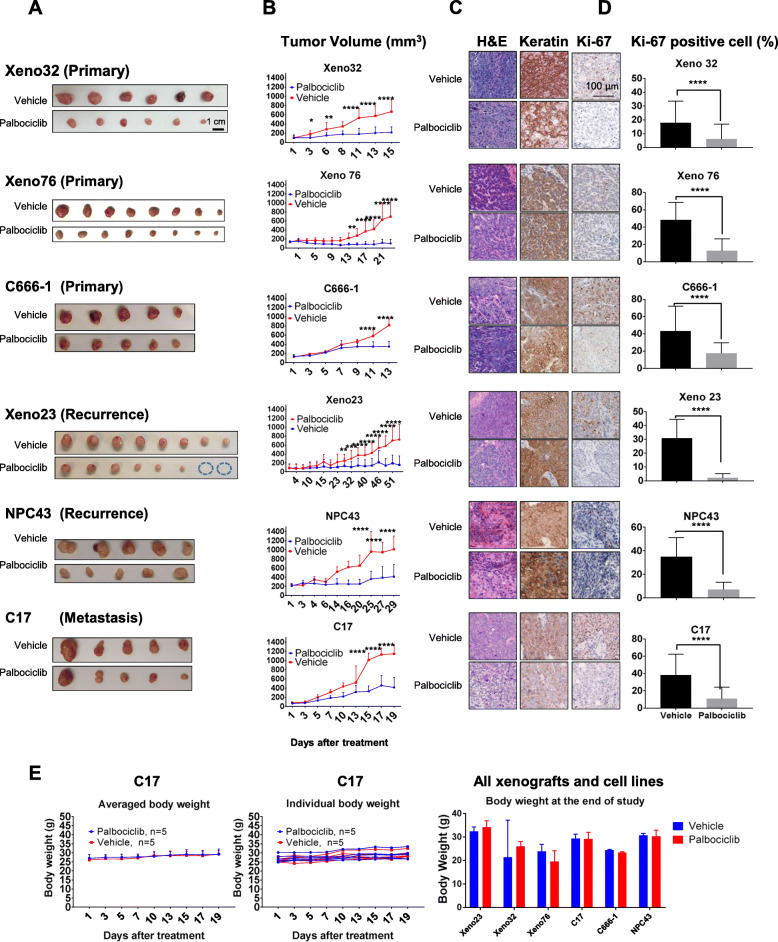
Fig. 2.
Palbociclib-mediated inhibition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) xenograft growth in vivo in NOD-SCID mice. Different NPC xenograft models were treated with palbociclib at a dose of 75 mg/kg/day via oral gavage. a-d. Left panel: Excised subcutaneous tumors at the end of palbociclib treatment. Middle left panel: NPC tumor growth curves during palbociclib treatment, which was initiated when the subcutaneously injected or implanted NPC xenografts became palpable (100–200 mm3). The tumor size was calculated as the Length × Width × Height/2. Middle right panel: Hematoxylin-eosin staining and immunohistochemistry (IHC) analyses of NPC tissue slides. Right Panel: Statistical analysis of Ki-67-stained cells in the tumor sections. Represents a tumor that regressed completely after drug treatment. Enlarged images of tissues subjected to IHC are presented in Supplementary Figure S6. e. Left panel: Average body weights of C17 tumor-bearing mice were measured throughout the experiment. Middle panel: Individual body weights of C17 tumor-bearing mice. Right panel: Bar chart of average body weights in the treatment and vehicle groups of all NPC xenografted models. P < 0.0001 ****, p < 0.001***, p < 0.005**, p < 0.01*