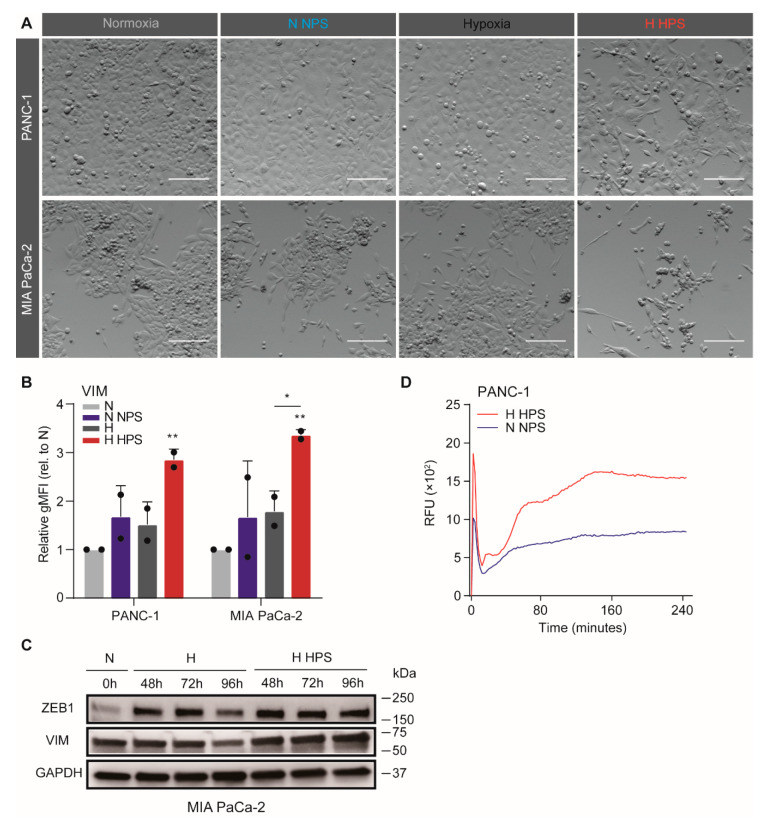
Figure 3.
Soluble compounds released by hypoxia-activated stellate cells confer invasive phenotypes in tumor cells. (A) PS1 supernatant was harvested after 72-h hypoxia (or normoxia control) to generate hypoxic PS1 supernatant (HPS) and normoxic PS1 supernatant (NPS). Example images of PANC-1 (upper row) and MIA PaCa-2 (lower row) cells exposed to 3 days of NPS/DMEM under normoxia, or with HPS/DMEM under hypoxia (brightness and contrast of the photos were adjusted). Scale bar: 50 µm. (B) Expression of VIM in PDAC cells was measured by flow cytometry and values were normalized to normoxic unconditioned medium group. Data show the average gMFI ± S.E.M. (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). (C) MIA PaCa-2 cells were incubated under conditions of H or H HPS for indicated times with normoxic incubation as a control. Cells were processed for Western blotting, using antibodies against ZEB1 and vimentin (VIM). GAPDH was used as loading control. (D) Transwell migration assays were performed on PANC-1 cells following treatments with NPS and normoxia, or HPS and hypoxia. 1% FCS was used as a chemoattractant. Migration curves are plotted with S.E.M. and corrected for no attractant controls (medium without FCS).