An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.
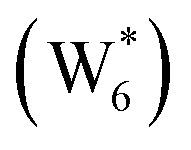 . (b) Gibbs free energy of adsorption (373 K) for ethanol monomer and dimer species at H2O coverages corresponding to the local minima of (a) and compared to ethanol monomer and dimer adsorption in the gas phase. W(intra) refers to intrapore water at other pure H2O clusters and is calculated from the intensive Gibbs free energy of water within the Beta pore. (c) Representative geometries of the stable water cluster
. (b) Gibbs free energy of adsorption (373 K) for ethanol monomer and dimer species at H2O coverages corresponding to the local minima of (a) and compared to ethanol monomer and dimer adsorption in the gas phase. W(intra) refers to intrapore water at other pure H2O clusters and is calculated from the intensive Gibbs free energy of water within the Beta pore. (c) Representative geometries of the stable water cluster 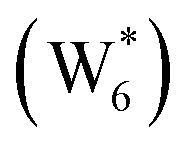 , ethanol monomer cluster
, ethanol monomer cluster  , ethanol dimer cluster
, ethanol dimer cluster 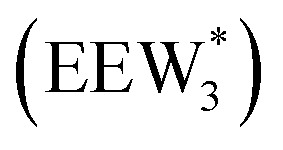 , and the ethanol–water dimer cluster formed by adsorption of one ethanol molecule at the stable monomer cluster
, and the ethanol–water dimer cluster formed by adsorption of one ethanol molecule at the stable monomer cluster  .
.