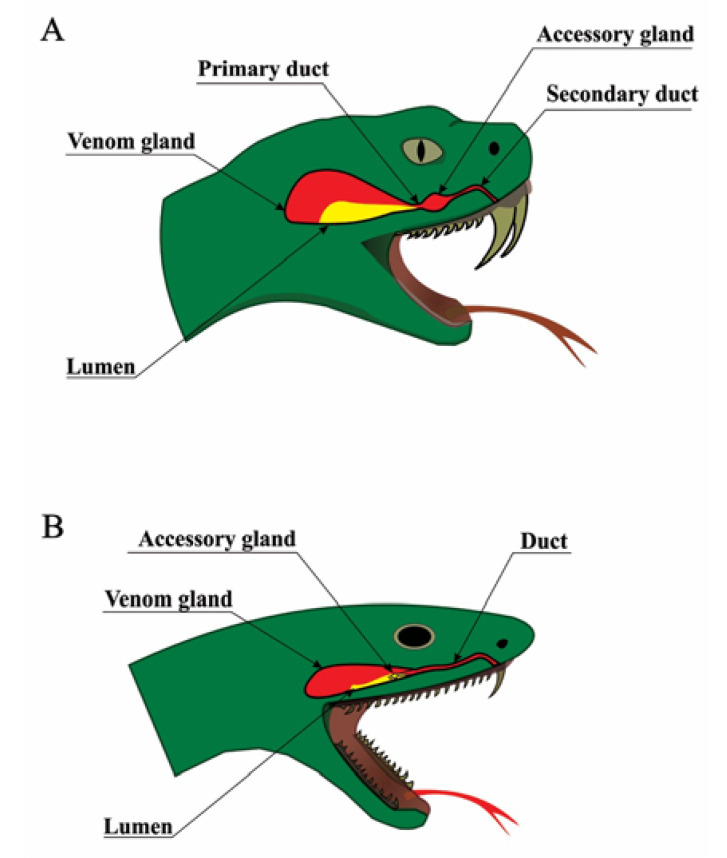
Figure 1.
Snake venom delivery systems. Schematic anatomy of snake venom delivery systems. (A) Viperidae venom system: The venom gland is triangular and large; the lumen is voluminous and can store high quantities of venom; the lumen forms the primary duct, which is connected to an accessory gland and finally to the secondary duct and the fang. (B) Elapidae venom system: The venom gland is oval; the lumen is narrow, and the majority of venom is stored in the secretory cells rather than the lumen; the accessory gland is placed in the distal part of the venom gland and has only one duct.