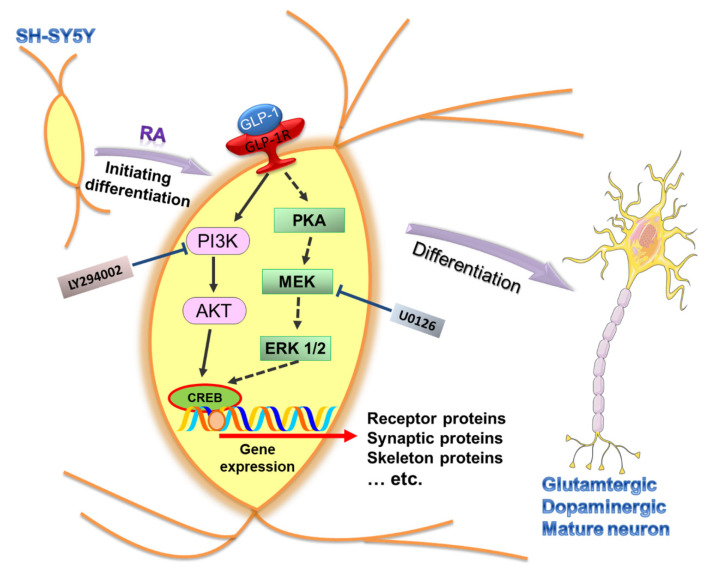
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram illustrating the downstream signaling of activated GLP-1R for regulating the SH-SY5Y neuronal differentiation. The expression of GLP-1 receptors (GLP-1Rs) has been seen in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and is involved in neuronal differentiation. Stimulation of GLP-1Rs triggers two downstream signaling axes, including PI3K-AKT (filled-line arrow) and PKA-ERK (dotted-line arrow). The specific inhibitors, LY294002 and U0126, were used to suppress the activity of PI3K and MEK, respectively. Our study’s overall results suggested that PI3K-AKT is the dominant downstream signaling axis regulating SH-SY5Y differentiation. In addition, the cells tend to develop into glutamatergic and dopaminergic neurons in GLP-1 induced neuronal differentiation. (RA: retinoic acid; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA: protein kinase A; MEK: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; ERK 1/2: mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 and 2; PI3K: phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; AKT: protein kinase B; CREB: cAMP response element binding protein).