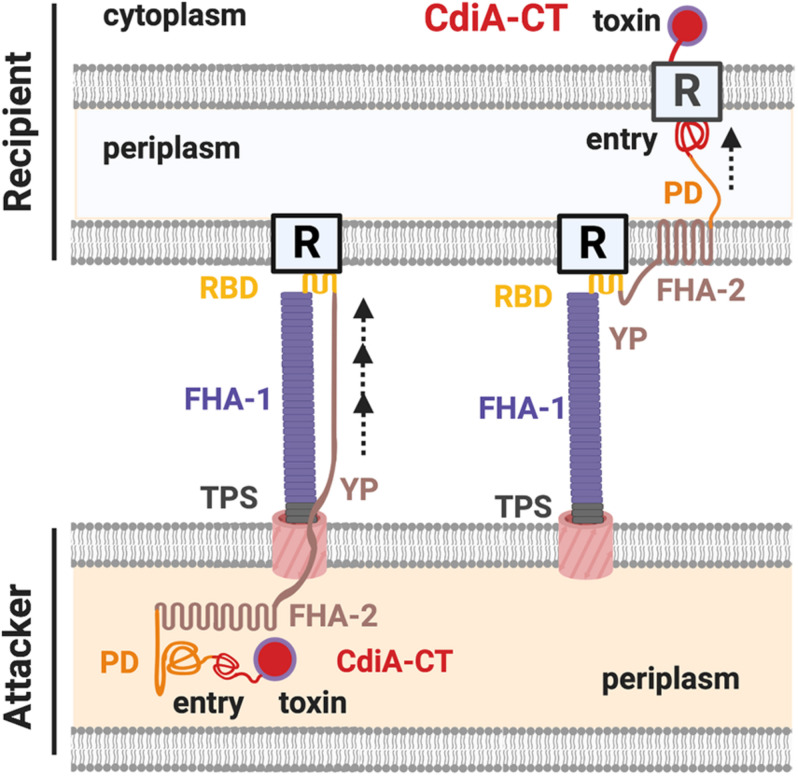
FIGURE 2.
The CdiA domains and the contact-dependent inhibition (CDI) working model. The domains of a CdiA from the N-terminus are the conserved two-partner secretion (TPS) transport domain, the filamentous hemagglutinin domain 1 (FHA-1), the receptor-binding domain (RBD), the Tyr/Pro-enriched (YP) domain, the second FHA domain (FHA-2), the pre-toxin (PD) domain, and the C-terminus toxin domain (CdiA-CT). The CdiA-CT is further divided into the N-terminus entry subdomain and the C-terminus toxin domain. In the resting state, the FHA-2, PD, and the CdiA-CT remain in the attacker cell, while the TPS, FHA-1, RBD, and the YP domains are exposed in the extracellular milieu of the cell surface. Upon recognizing the outer membrane (OM) receptor (R) of a recipient cell by the RBD domain of CdiA, FHA-2 exposes and assembles into the recipient OM and translocates the CdiA-CT into the recipient periplasm. The entry domain then recognizes the IM receptor and translocates the toxin domain into the cytoplasm, where the toxin exerts its toxicity.