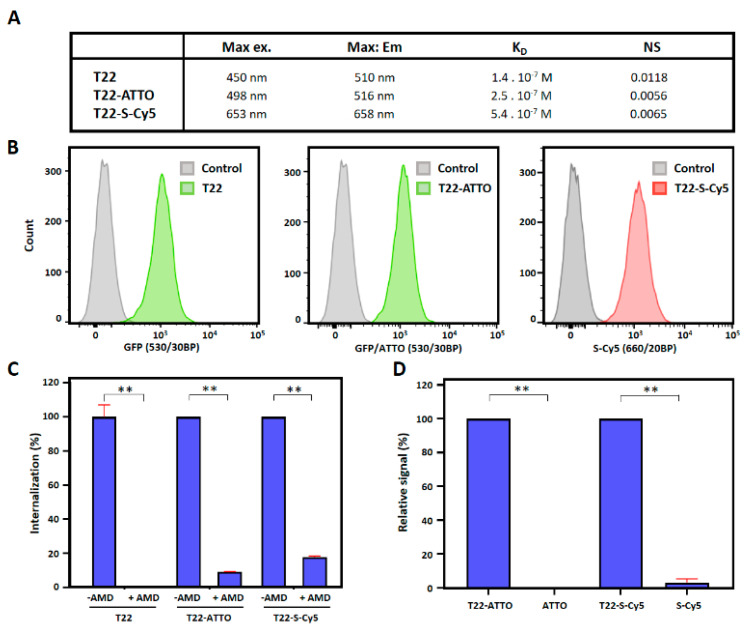
Figure 3.
CXCR4-mediated cell internalization of nanoconstructs. (A) Biophysical properties of T22-GFP-H6 (T22), T22-GFP-H6-ATTO (T22-ATTO) and T22-GFP-H6-S-Cy5 (T22-S-Cy5) nanoparticles. (B) T22-GFP-H6 (T22) nanoparticles, and labeled T22-GFP-H6-ATTO (T22-ATTO) and T22-GFP-H6-S-Cy5 (T22-S-Cy5) nanoparticles internalization in cultured CXCR4+ Toledo cells monitored by flow cytometry upon 1 h of exposure. Grey peak overlays show control cells auto-fluorescence. 530/30BP indicates 515–545 nm bandpass filter, and 660/20BP indicates 650–670 nm bandpass filter. (C) CXCR4-mediated internalization in presence and absence of the CXCR4 specific antagonist AMD3100, upon 1 h of exposure. (D) Background fluorescence signal upon incubation of free ATTO488 (ATTO) and Sulfo-Cy5 (S-Cy5) in Toledo cells for 1 h. Fluorescence signal of free samples is shown relative to their respective nanoconjugate signals. Significant differences at p < 0.01 are indicated as **.