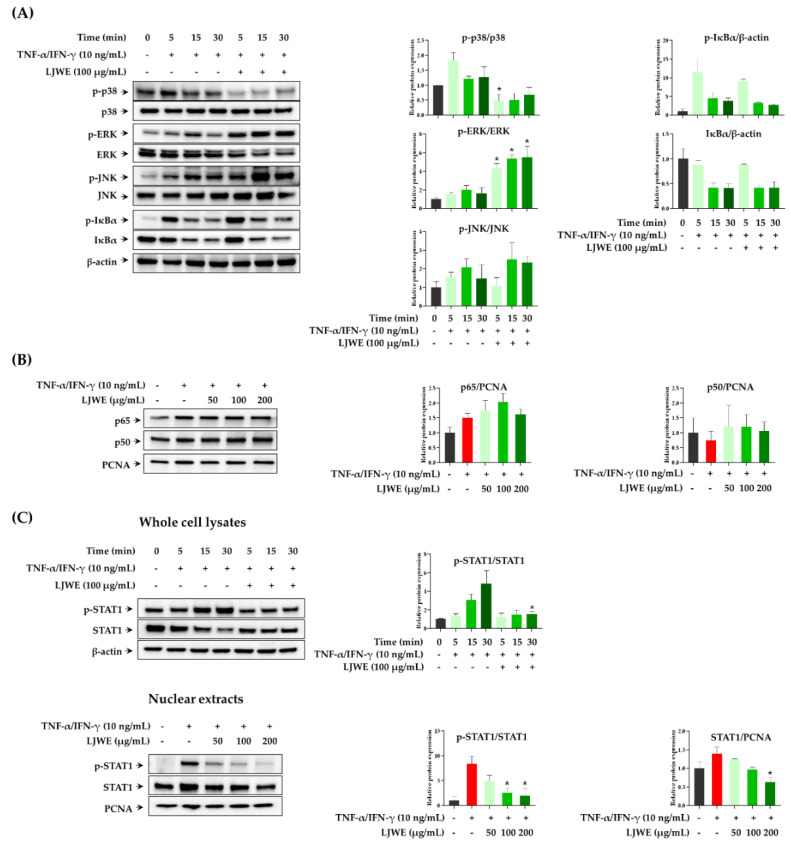
Figure 2.
Modulatory effects of LJWE on mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) signaling pathways in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α/interferon (IFN)-γ-stimulated HaCaT cells. The cells were pretreated with (+) or without (−) LJWE for 1 h and incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of TNF-α/IFN-γ (each 10 ng/mL) for 5, 15, and 30 min. Western blotting was performed to determine the phosphorylation and degradation of p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), Inhibitor kappa B-alpha (IκBα), and STAT1 in whole cell lysates. The translocation of NF-κB and STAT1 was determined 3 h post-TNF-α/IFN-γ treatment. (A) Effects of LJWE on the phosphorylation and degradation of MAPKs in whole cell lysates. (B) Effects of LJWE on the nuclear translocation of NF-κB. (C) Effects of LJWE on the activation (upper panel) and nuclear translocation (lower panel) of STAT1. * p < 0.05 vs. control treated with vehicle. PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen.