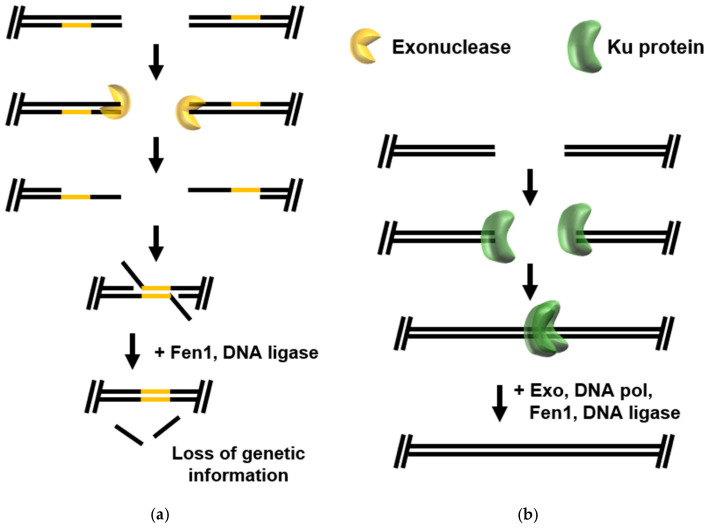
Figure 3.
“Error-prone” double-strand break (DSB) repair pathways in Archaea: (a) In microhomology-mediated end joining (MMEJ), small regions of microhomology (yellow) are revealed by exonuclease activity; annealing and subsequent processing by flap endonuclease and DNA ligase often results in the loss of genetic information. (b) Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) in some archaeal species relies on recognition of broken ends by Ku which brings broken ends together, where exonuclease activity produces complementary ends for conclusion of DNA repair. The proteins that mediate NHEJ in many archaeal clades have not yet been defined.