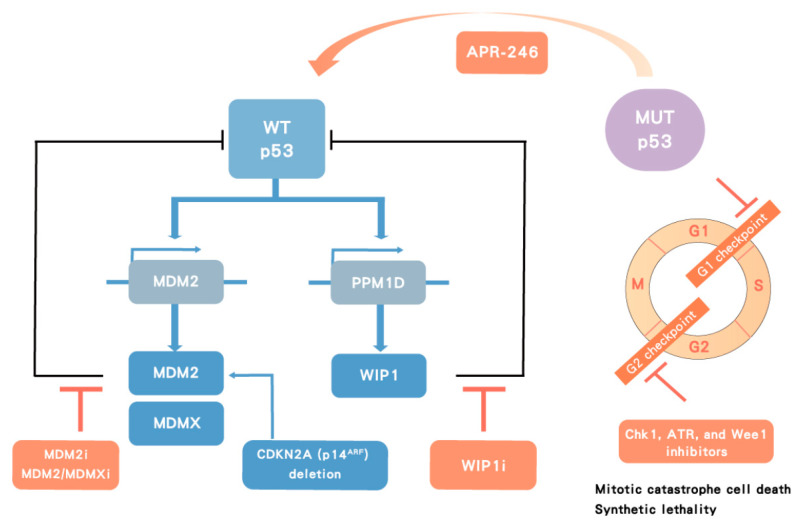
Figure 6.
Therapeutic strategy targeting p53. In p53 wild-type (WT) cancers, p53 transactivates its negative regulators, MDM2 and wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (WIP1), which in turn inhibit p53 function. MDMX cooperates with MDM2 to degrade p53. MDM2 inhibitors (MDM2i), dual MDM2/MDMX inhibitors (MDM2/MDMXi) and WIP1 inhibitors (WIP1i) target negative regulators of p53 leading to p53 stabilization and activation. In contrast, p53 mutant (MUT) tumors can potentially be treated with a direct activator, such as APR-246, or indirectly with Chk1, ataxia telangiectasia related (ATR), and Wee1 inhibitors, which lead to cell death by mitotic catastrophe in MUT p53 cancers.