FIGURE 1.
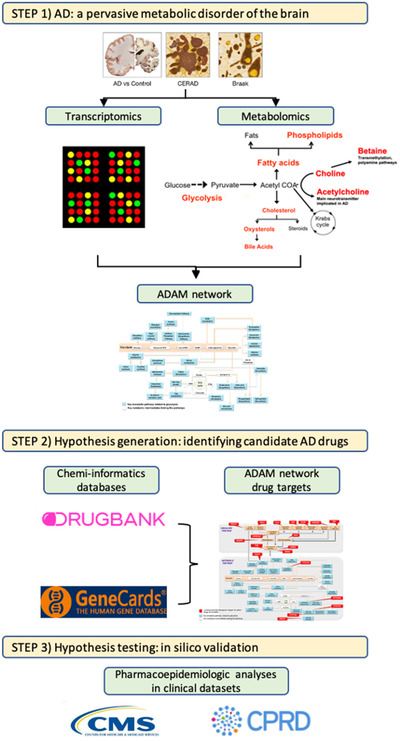
Drug Repurposing for Effective Alzheimer's Medicines (DREAM) study design. Schematic workflow of the DREAM study. Step 1: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a pervasive metabolic disorder of the brain. Targeted metabolomics and transcriptomic analyses of brain tissue samples reveals dysregulation in multiple metabolic pathways related to abnormal glycolysis in AD. These pathways are proposed to be components of the Alzheimer's Disease Aberrant Metabolism (ADAM) network (see Figure 2a) and are associated with severity of AD pathology. Step 2: Hypotheses generation: identifying candidate drugs for Alzheimer's disease and related disorders (ADRD). Chemi‐informatics databases such as GeneCards and DRUGBANK are used to determine whether genetic regulators of biochemical reactions within the ADAM network (see Figure 2b) are targeted by approved drugs for non–ADRD‐related indications. Step 3: Hypotheses testing: in silico validation of candidate ADRD drugs. Pharmacoepidemiologic analyses in complementary population‐based clinical datasets (Centers for Medicare and Medicad Services, United States; Clinical Practice Research Datalink, United Kingdom) are used to test efficacy of candidate ADRD treatments
