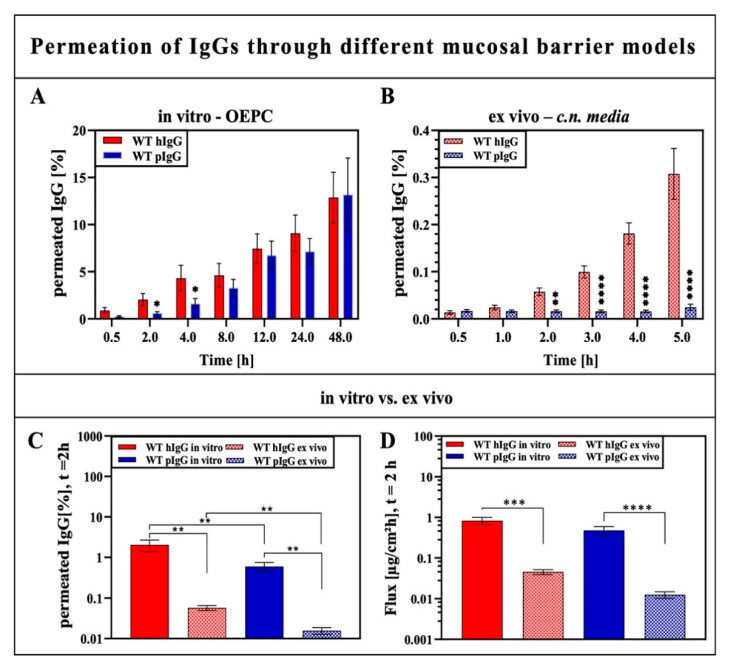
Figure 2.
Cumulated permeation of allogenic porcine serum IgG (pIgG) and xenogenic human IgG (hIgG) through in vitro porcine olfactory epithelial primary cells (OEPC) and ex vivo porcine olfactory mucosa (conchae nasalis media (c.n. media)). (A) Percentage permeation of wild-type hIgG (WT hIgG) and porcine serum IgG (WT pIgG) through olfactory epithelial primary cells (OEPC) over 48 h. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. N = 4, n = 21. (B) Percentage permeation of WT hIgG and WT pIgG through excised nasal mucosa tissue explants (ex vivo—c.n. media) over 5 h. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. WT hIgG: N = 4, n = 29, WT pIgG: N = 4, n = 12. (C) Comparison of percentage permeated IgG through the OEPC in vitro model and the ex vivo model after 2 h. (D) Comparison of the flux of the IgGs through the in vitro and the ex vivo model. The significance was analyzed by unpaired t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.0001; **** p < 0.00001, error bars represent mean ± SEM.