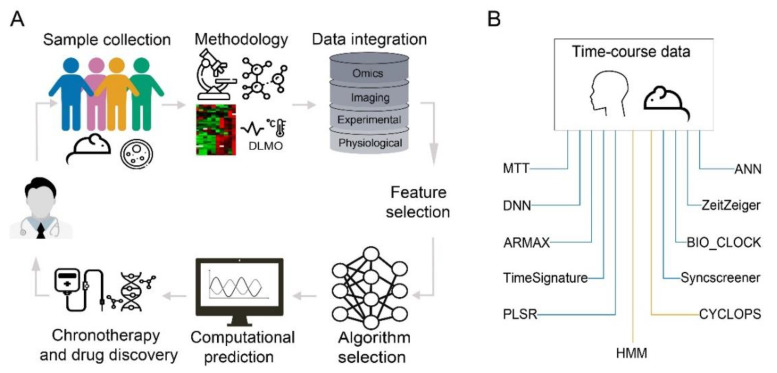
Figure 4.
Schematic workflow of a computational prediction pipeline using machine learning based algorithms and possible applications in personalized medicine. (A) Inter-disciplinary data collected from human subjects, animal and cell line models are integrated using computational methods. The integrated data is then examined and features (variables) depicting potentially relevant information for the prediction model are selected. Based on the complexity of features and the prediction goal, an algorithm is selected and the computational prediction takes place. The prediction model can produce knowledge that serve as the basis for chronotherapy planning. (B) Schematic representation of supervised (blue lines) and unsupervised (yellow lines) machine learning algorithms used to predict circadian parameters based on genomics or physiological data.