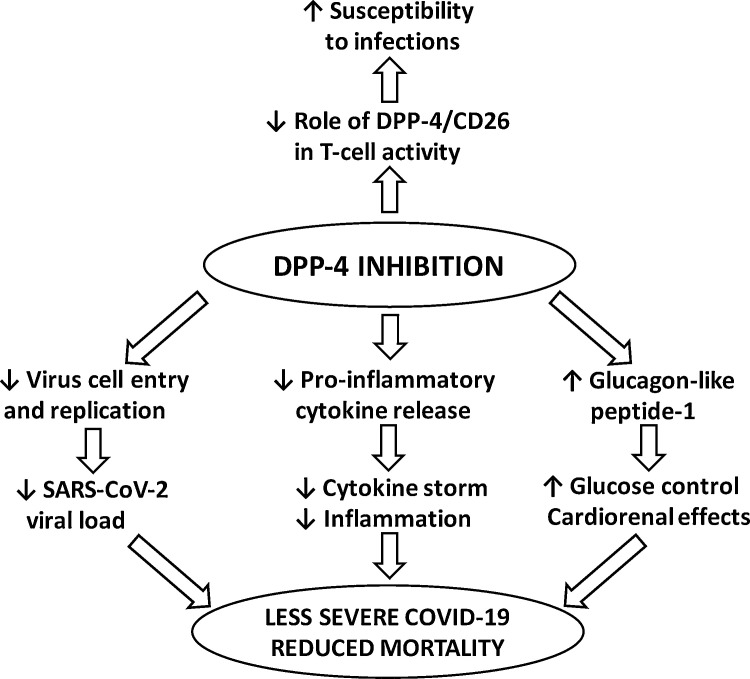
Fig. 1.
Hypothetical interactions between dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibition and infections such as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients with type 2 diabetes: (upper) initial concerns for a possibly increased risk of infection; (lower) recent expectations that DPP-4 inhibition might improve the prognosis of patients exposed to COVID-19 through various yet-to-be-confirmed mechanisms. SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.