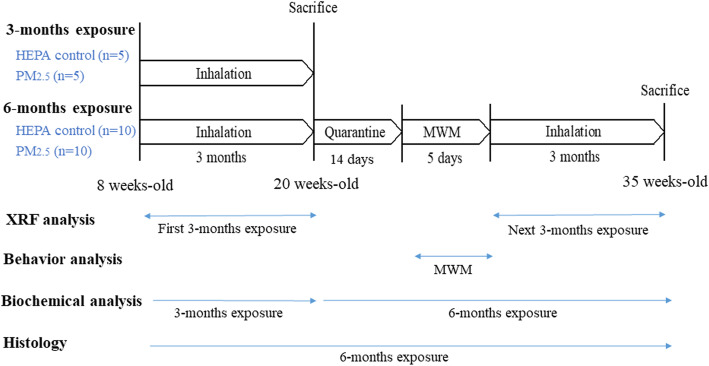
Fig. 1.
Overview of the experimental design for investigating the effects of fine particulate matter (PM2.5; PM with an aerodynamic diameter of < 2.5 μm) on neurotoxicity in spontaneously hypertensive (SH) rats. The whole bodies of 8-week-old SH rats in the high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) and PM2.5 groups were exposed to urban PM2.5 for 3 and 6 months. In the 6-month group, a Morris water maze (MWM) was used to observe behavioral changes in SH rats after 3 months of exposure. After the MWM, rats were followed up for a subsequent 3 months of exposure to PM2.5. Rats were euthanized after 3 or 6 months of exposure for biochemical analyses. The 6-month group was histologically examined. Additionally, urban PM2.5 was collected onto Teflon filters for metal analyses