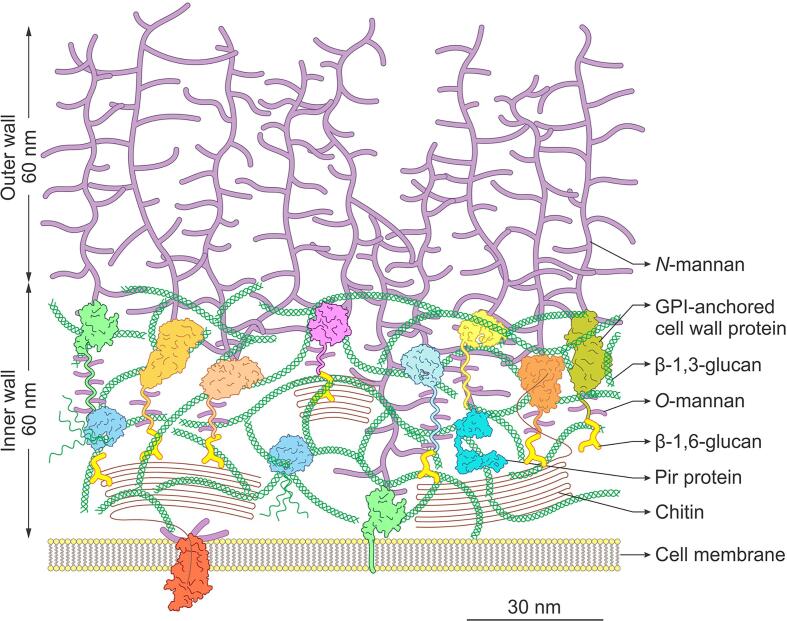
Fig. 6.
Refined, to-scale model of the C. albicans cell wall. The inner layer of the cell wall is comprised of chitin microfibrils (brown) interspersed with triple and single helices of β(1,3)-glucan (green). Mannosylated cell wall proteins are distributed throughout the inner cell wall layer, with a small proportion in the cell membrane. The N-mannan structures (purple) attached to cell wall proteins form the outer fibrillar layer of the cell wall. GPI-anchored cell wall proteins are abundant and have a globular domain to which long N-mannan structures are attached, and a stalk region to which short O-mannans (purple) are attached. Examples shown in the figure are Als3 (chrome yellow), Als9-2 (light olive green), Sod5 (mint green), Sap1 (lemon yellow) and Sap3 (sky blue), an endo-glucanase (beige), an exo-glucanase (pink) and a chitinase (orange). These are covalently linked to chitin and β(1,3)-glucan via β(1,6)-glucan linkages (yellow). Pir cell wall proteins (turquoise) are less abundant and are N-mannosylated and covalently linked to β(1,3)-glucan via an unknown alkali-sensitive bond. A partial chitin synthase enzyme with its catalytic core and transmembrane domain is depicted in the membrane (red). The scale bar represents 30 nm.