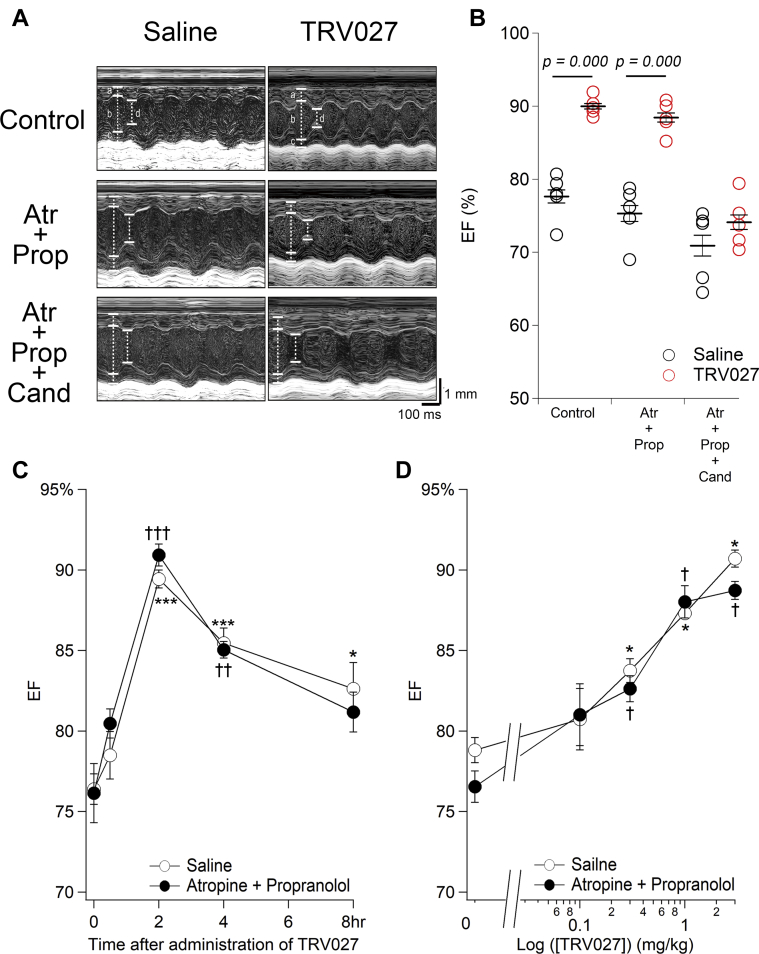
Figure 1.
TRV027 Causes a Long-Acting Positive Inotropic Effect Through AT1R in a Dose-Dependent Manner in the Neonatal Mouse Heart
(A) Representative M-mode ultrasoundcardiogram recorded from neonatal mice treated with saline (left column) or TRV027 (right column). UCG was recorded 2 h after intraperitoneal injection of saline or TRV027 (3 mg/kg) (top row). Then, atropine (Atr) (1 mg/kg) plus propranolol (Prop) (1 mg/kg) was added, and the measurements were repeated 10 min later (middle row). Furthermore, candesartan (Cand) (3 mg/kg) was added, and the measurements were once again repeated 20 min later (bottom row). In these traces, a, b, c, and d indicate interventricular septum end-diastolic thickness, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, posterior wall end-diastolic thickness, and end-systolic diameter, respectively. (B) The values of ejection fraction (EF) measured under each condition. Symbols indicate each data. The p value was calculated with unpaired Student’s t test. (C) Indicated time after injection of TRV027 (3 mg/kg) to neonatal mice, saline (open circles) or atropine + propranolol (1 mg/kg each) (closed circles) was added. Then, EF was measured 10 min later. Statistical significance of the time-dependent change in EF was analyzed with 1-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett’s test. ∗†p < 0.05; ∗∗††p < 0.01; ∗∗∗†††p < 0.001 versus 0 h in the saline and Atr + Prop groups, respectively. Neither significant effect of atropine + propranolol nor interaction between time and drugs was indicated with 2-way analysis of variance. n = 5 to 6 in each group. (D) Two hours after injection of indicated doses of TRV027 to neonatal mice, saline (open circle) or Atr + Prop (closed circle) was added. Then, EF was measured 10 min later. The p value was calculated with paired Student’s t test. ∗†p < 0.05 versus 0 mg/kg in the saline and atropine + propranolol groups, respectively. n = 3 in each group.