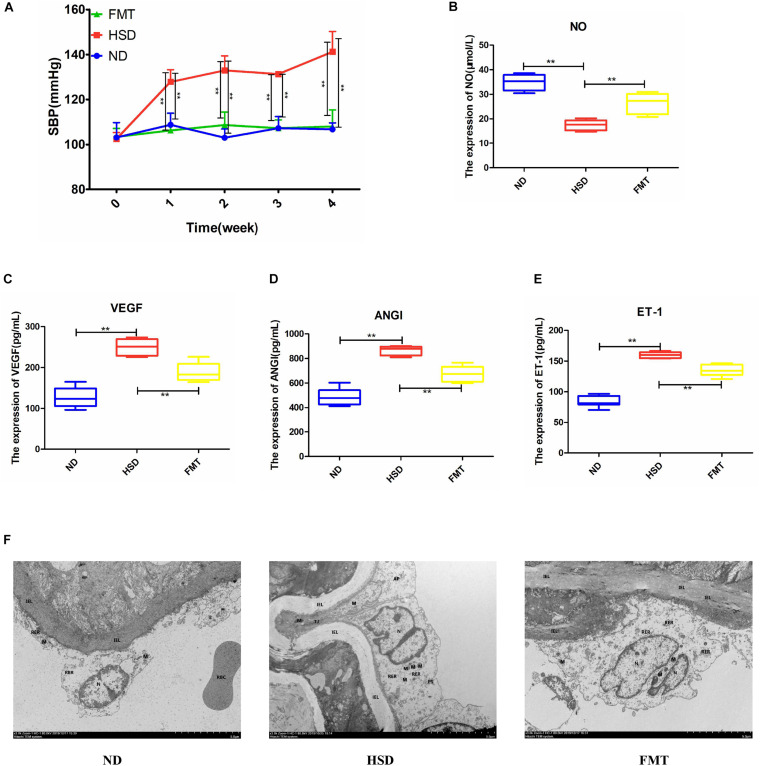
FIGURE 5.
FMT using Atf4± mice fecal microbiota improved SBP and altered expression of endothelial function-related factors in high-salt-induced hypertensive mice. (A) FMT maintained SBP. (B) FMT upregulated the expression of NO. (C) FMT downregulated the expression of VEGF. (D) FMT downregulated the expression of ANGI. (E) FMT downregulated the expression of ET-1. (F) Examination of endothelial morphology by transmission electronic microscope (TEM). IEL, internal elastic lamina; N, nucleus; M, mitochondrion; RER, rough endoplasmic reticulum; TJ, tight junction; AP, autophagy. Data are presented as mean ± SD; **p < 0.01, n = 6–8; statistical comparisons were performed using Student t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). FMT, fecal microbiota transplantation; SBP, systolic blood pressure; NO, nitric oxide; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ANGI, angiotensin I; ET-1, endothelin-1; ND, WT mice with natural diet; HSD, WT mice with high-salt diet.