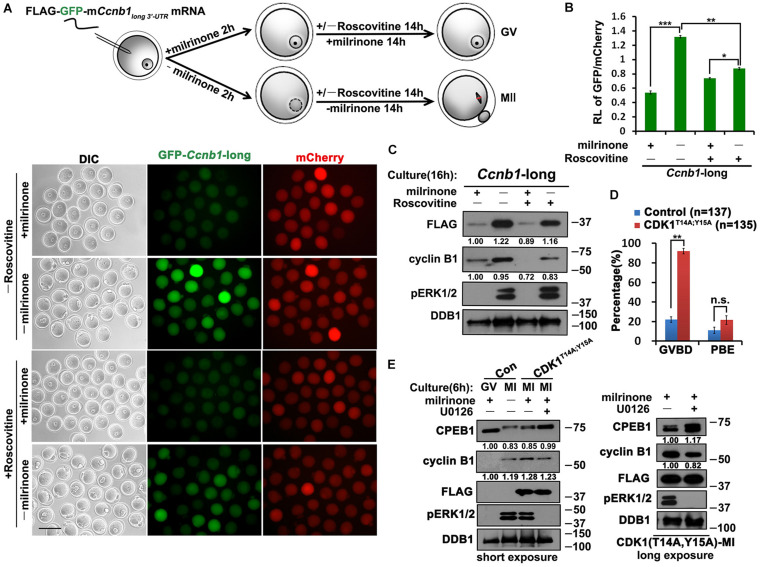
FIGURE 3.
Role of CDK1 in the translational activation of Ccnb1 mRNAs. (A) Fluorescence microscopy results revealing the expression levels of Flag-Gfp-Ccnb1long 3′–UTR mRNA in oocytes with different roscovitine (100 μM) treatment. For each set of data, 50 oocytes were gathered. Plotting scale: 100 μm. (B) Relative fluorescence intensity of GFP relative to mCherry in (A). Data were analyzed by mean ± SEM: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) Western blot analysis results revealing translational levels of the reporter mRNA as well as endogenous cyclin B1 in (A). For each set of data, 80 oocytes were gathered and loaded. (D) GVBD and PBE rates of oocytes microinjected with mRNAs encoding non-inhibitable CDK1 (T14A;Y15A) and cultured for 14 h. The accurate number of oocytes analyzed is labeled (n). DDB1 was used for a control. Numbers under blot bands indicate the intensity of each band. Data were analyzed by mean ± SEM: **P < 0.01. n.s. indicates non-significant. (E) Western blot analysis results showing levels of indicated proteins in oocytes overexpressed mRNAs encoding CDK1T14A;Y15A and cultured with different milrinone and U0126 (20 μM) treatment. For each set of data, 70 oocytes were gathered and loaded. DDB1 was used for a control. Numbers under blot bands indicate the intensity of each band.