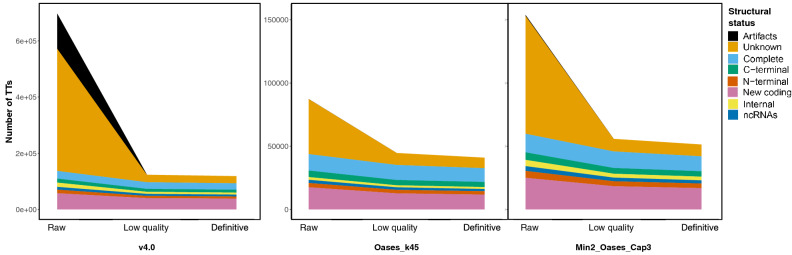
Figure 1.
Distribution of TTs grouped by their structural status in the three assembling approaches: v4.0, Oases_k45 and Min2_Oases_Cap3. “Raw” refers to transcriptomes as in Table 2. “Low quality” results from removal of unmapped and atypical TTs in Table 3. “Definitive” are also devoid of low quality TTs in Table 3. Structural statuses for TTs are ‘Artifacts’ (not supported by mapped paired-end reads), ‘Unknown’ (without any sequence similarity in databases), ‘Complete’ (with a complete CDS (coding sequence) region), ‘C-terminal’ (with a C-terminal part of a CDS), ‘N-terminal’ (with a N-terminal part of a CDS), ‘Internal’ (internal CDS identified, lacking both N- and C-terminus), ‘New coding’ (can code for an unidentified protein), and ‘ncRNA’ (identical to ncRNA precursor in databases).