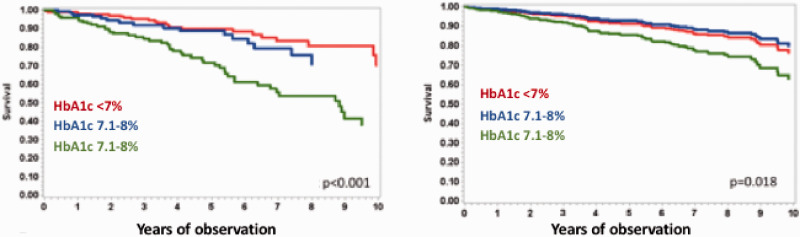
Figure 1.
Effect of glycaemic control on long-term prognosis (composite of cardiovascular death, urgent heart transplant, or left ventricular assist device implantation) in diabetic heart failure patients at baseline (panel on the left) and after correction for multiple confounders (ejection fraction, oxygen uptake at peak exercise, haemoglobin, minute ventilation/carbon dioxide production relationship slope, renal function and sodium plasma levels) (panel on the right).
Data from the MECKI score database. Modified from Johansson et al.25
HbA1c: glycated haemoglobin.