Fig. 4.
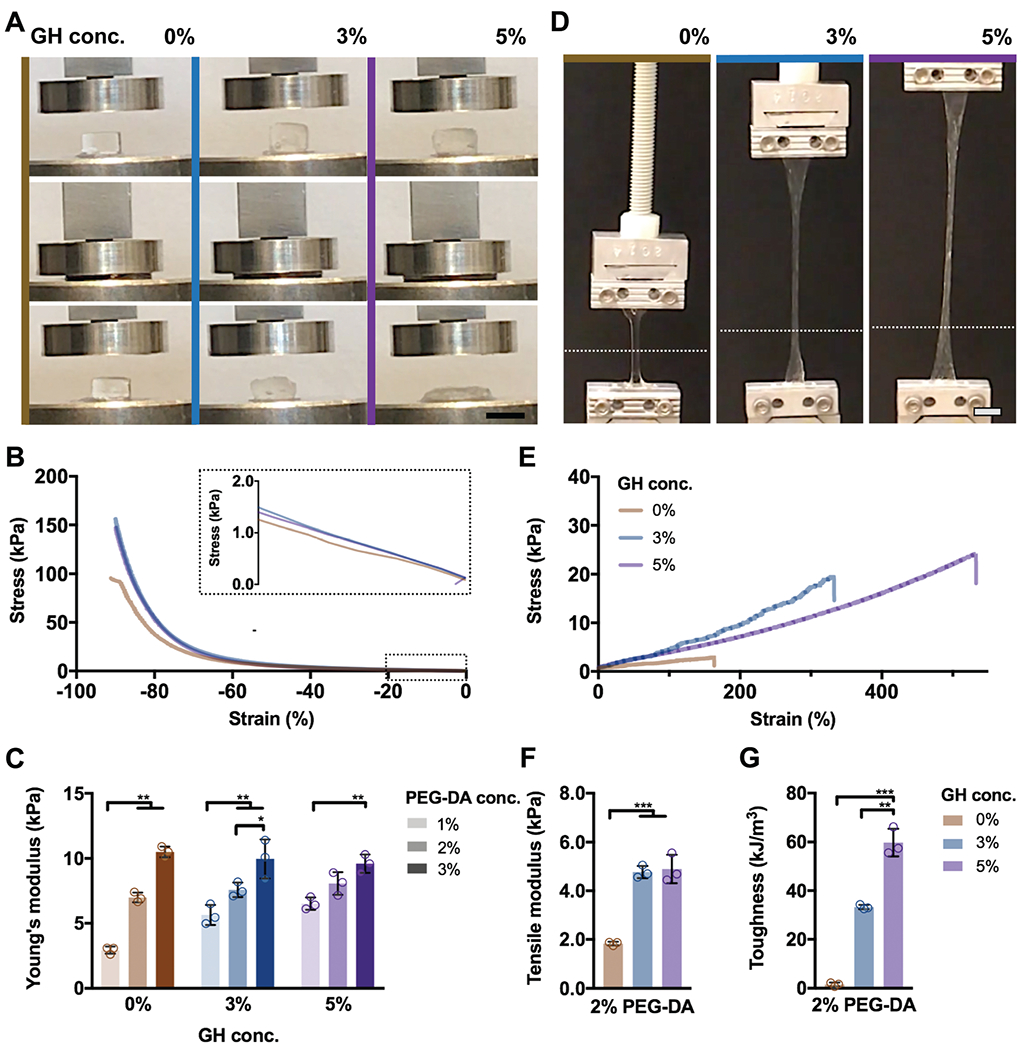
DN hydrogels exhibit high mechanical strength and toughness. (A–C) Compressive and (D–G) tensile testing of DN hydrogels (PEG-fibrinogen (8.5 mg mL−1) plus 2% PEG-DA) without (0%) or with (3%, 5%) GH of different concentrations. (A) Images of DN hydrogel compressive testing (scale bars 5 mm) and corresponding (B) stress–strain profiles (0.5 N min−1) and (C) Young’s moduli (n = 3 replicates per group, mean ± SD, **p ≤ 0.01) for DN hydrogels. (D) Images of DN hydrogel tensile testing, where the starting position of the top grid is indicated (dotted line, scale bars 5 mm) and corresponding (E) stress-strain profiles (5 mm s−1), (F) tensile moduli, and (G) toughness for DN hydrogels (n = 3 replicates per group, mean ± SD, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001).
