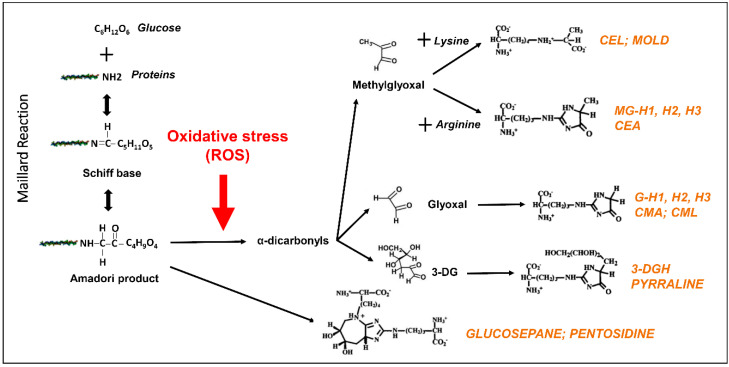
Figure 1.
Production of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) is accelerated under oxidative stress. AGEs are derived from sugars or dicarbonyls generated from carbohydrate metabolism through different chemical routes including the Maillard reaction. The excess of reactive oxidative species (ROS) promotes the production of different AGEs from dicarbonyls (methylglyoxal, glyoxal, or 3-deoxyglucosone (3-DG). AGEs are highlighted in orange. CML: Nε-(carboxymethyl)-lysine; CMA: Nε-(carboxymethyl)-arginine; 3-DG: 3-deoxyglucosone; 3-DGH: GH-1,2,3: Glyoxal-derived hydroimidazolone; MGH-1,2,3: Methylglyoxal-derived hydroimidazolone; CEL: Nε-(carboxyethyl)-lysine; CEA: Nε-(carboxyethyl)-arginine; MOLD: Methylglyoxal-derived lysine dimer.