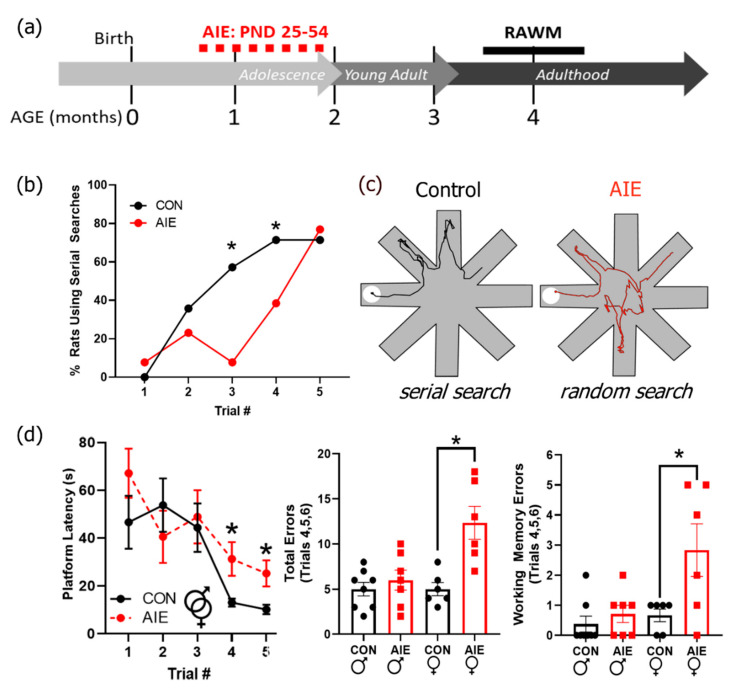
Figure 3.
Adolescent intermittent ethanol (AIE) impairs problem-solving flexibility in the radial arm water maze (RAWM). (a) Timeline of RAWM paradigm. Rats underwent AIE or control gavage paradigms from PND 25–54. The RAWM was conducted later in adulthood (around 4 months of age). (b) Serial versus random search strategies were determined by a blind observer, as described in the methods. Controls increased employment of serial search strategies immediately after the first trial and increasingly employed serial searches on subsequent trials. AIE rats predominantly used random search strategies until trial three (males) and trial four (females), suggesting deficits in problem-solving strategy flexibility. (c) On the left is an example of typical run from a control rat using a serial search strategy (trial 5). On the right is an example run from an AIE rat using a random search strategy (trial 5). (d) AIE rats took longer to find the platform on the fourth and fifth runs of the first test day, suggesting a mild deficit in spatial learning. This effect is predominantly driven by an increase in the number of total errors made by AIE females. In addition, females tended to make more reference errors, suggesting deficits in working memory may be contributing to these results. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05.