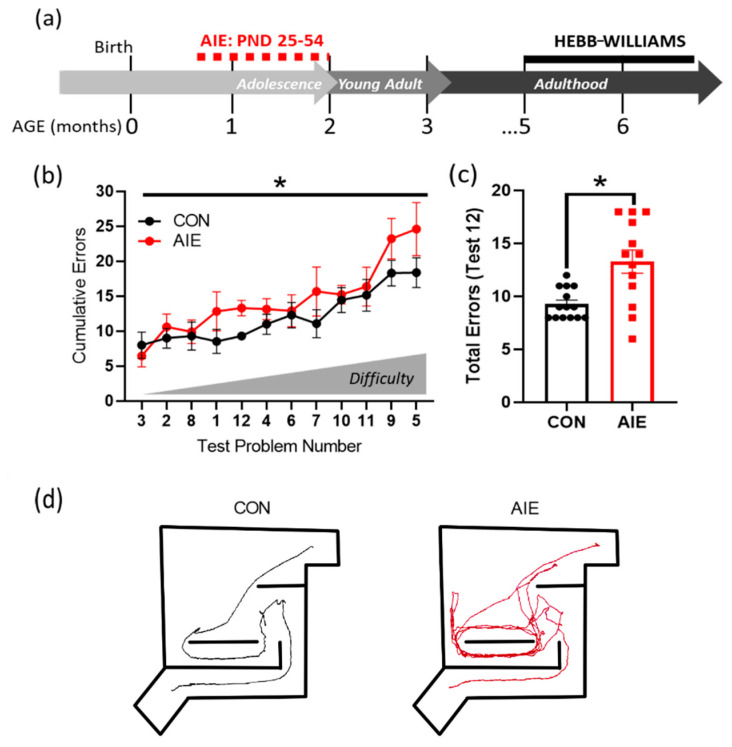
Figure 4.
AIE increases errors in the Hebb-Williams maze battery. (a) Timeline of Hebb–Williams testing paradigm. Rats underwent AIE or CON gavage paradigms from PND 25–54. The Hebb-Williams maze was conducted later in adulthood (5–6 months of age). Males were tested first, followed by females. (b) As shown, tests were ranked by difficulty. In general, AIE increased errors in the Hebb-Williams maze, with greater divergence evident with increasing difficulty. (c) An example distribution of the number of errors rats made on test 12. AIE significantly increased the number of cumulative errors across the eight trials. (d) Example runs taken from test 12 for control (left) and AIE (right). Controls, on average, did not repeat errors, unlike AIE rats, which perseverated on the same incorrect turns. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05.