Figure 4.
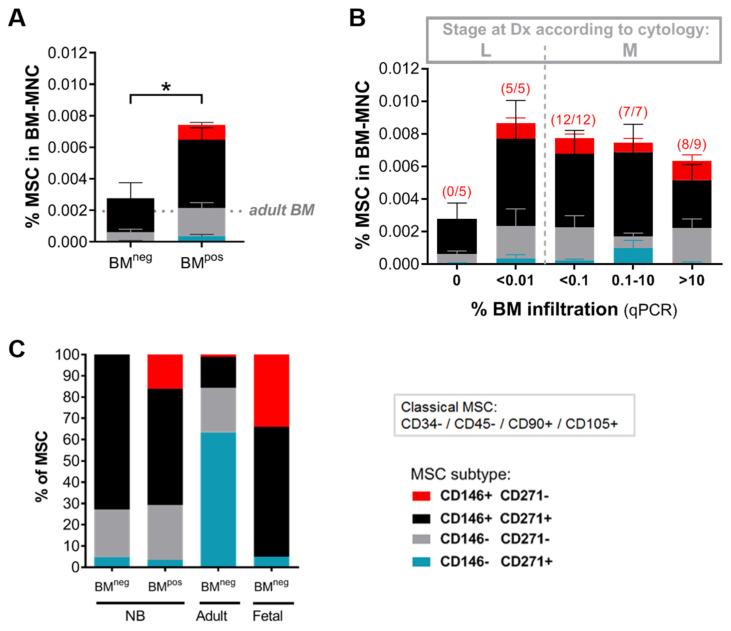
The metastatic BM niche contains a specific MSC subtype. Metastatic disease in the BM is defined based on qPCR positivity as BMpos and qPCR negativity as BMneg (A) Frequency of MSCs in diagnostic BM aspirates of patients relative to the number of BM-mononuclear cells (BM-MNC) (BMpos n = 33, BMneg n = 5). MSCs are detected by flow cytometry using the classical MSC-panel (CD34−, 45−, 90+, 105+) and subtype distribution is analyzed based on CD146 and CD271 expression. Dotted line marks average MSC level in control adult BM (n = 5). (*) p < 0.05. (B) MSC (-subtype) levels in BM samples grouped based on stage and extent of BM infiltration (as determined by qPCR). Patients were diagnosed as ‘localized’ when there was no evidence of metastases by 123I-MIBG scintigraphy and morphological examination of BM smears/biopsies. Based on RT-qPCR results, we classified them as negative (n = 5) or positive. qPCR positive localized BM samples (n = 5) all contain less than 0.01% tumor cells. For stage 4 NB-patients (i.e., with metastases) the extent of BM infiltration is classified as <0.1% (n = 12), 0.1–10% (n = 7), or >10% (n = 9). Number of BM samples positive for CD146+CD271− MSC is indicated in brackets above the bar. (C) Relative contribution of distinct MSC subtypes to the MSC compartment in diagnostic BM of NB-patients compared to fetal and adult BM. Adult MSCs: n = 4, fetal MSCs: n = 6. Data from fetal MSCs is adapted from Maijenburg et al., 2012 [36].