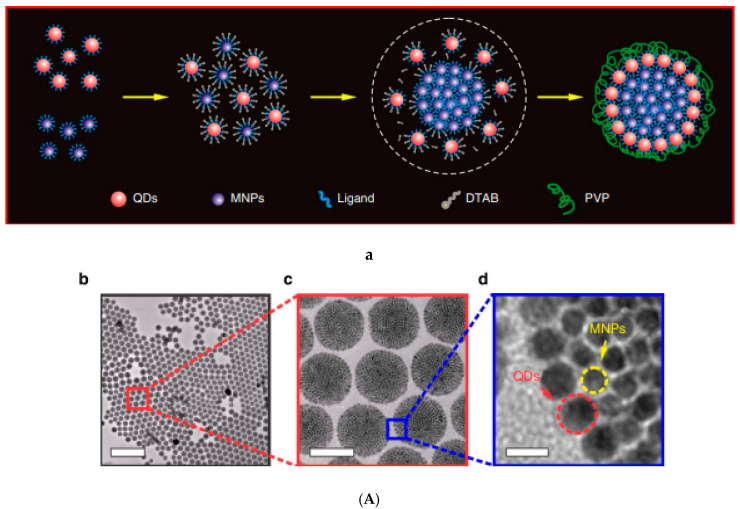
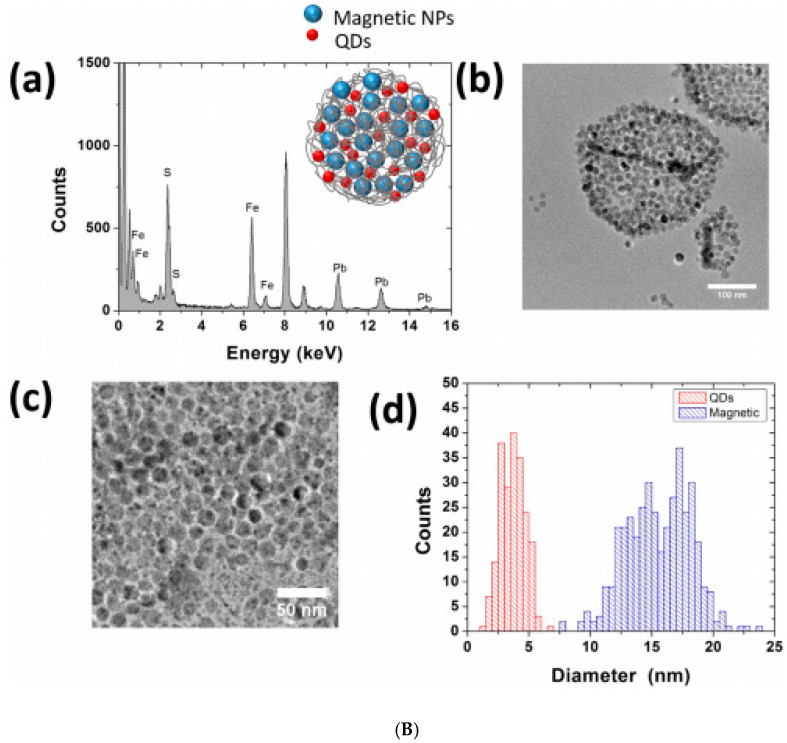
Figure 3.
Co-assembling quantum dots and magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) of a ferrofluid in a magnetoresponsive core–shell nanostructure. (A) Synthesis and characterizations of core–shell-structured supraparticles (CS-SPs). (a) Schematic of the formation of the CS-SPs. A set of TEM images of CS-SPs at different magnifications. Scale bars, 500 nm, 100 nm, and 10 nm (b–d). Ferrofluid: magnetite NPs in chloroform carrier. Characteristic sizes: 9.0 nm for QDs (CdSe-CdS) and 5.9 nm for magnetite NPs (reprinted by permission from Copyright Clearance Center: Springer Nature, Nature Communications [144], Copyright 2014); (B) (a) Compositional analysis (EDX) of a PLGA nanostructure denoting the presence of elements of both magnetic IONPs and QDs (PbS). (inset) Schematic diagram of the magnetic NPs and QDs in the PLGA nanostructure. (b) TEM image of a typical PLGA nanostructure. (c) A detailed TEM image of a PLGA nanostructure revealing the presence of two types of NPs inside the structure. (d) Size distribution of both types of particles obtained from TEM images. The size distribution corresponds to the sizes of the magnetic NPs (15 nm) and QDs (4 nm). Ferrofluid: oleic acid-coated magnetite NPs in hexane carrier. (reprinted with permission from [145]. Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society).