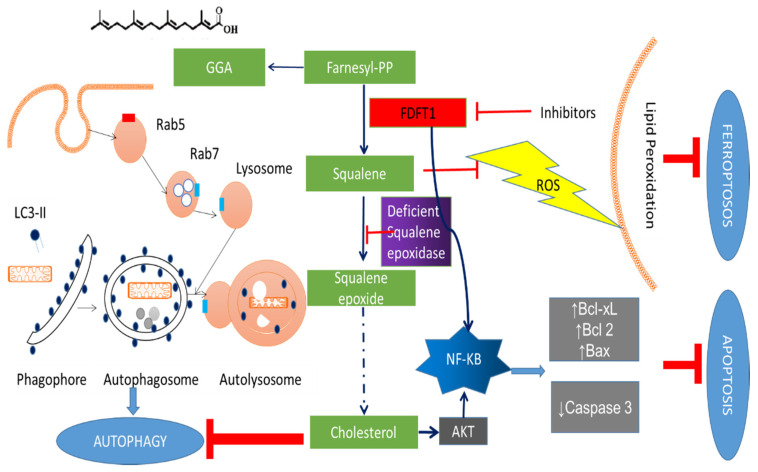
Figure 4.
The association between FDFT1 and cell death. FDFT1 is directly or indirectly associated with apoptotic signals. FDFT1 could directly activate NF-KB pathways or activate AKT through cholesterol synthesis. Activated NF-KB increases anti-apoptotic proteins, such as Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, and Bax and decreases pro-apoptotic proteins such as caspase-3, thereby blocking apoptosis signalling. In cancer cells with deficient squalene epoxidase, high expression of FDFT1 increased intracellular squalene levels, which protects the cell membrane from lipid peroxidation by ROS and further prevents the cell from entering the ferroptosis pathway. Furthermore, FDFT1 inhibition upregulates endogenous geranylgeranoic acid (GGA) content, which has been demonstrated to cause incomplete autophagy, and a decrease in cholesterol level also activates autophagy.