Fig. 3.
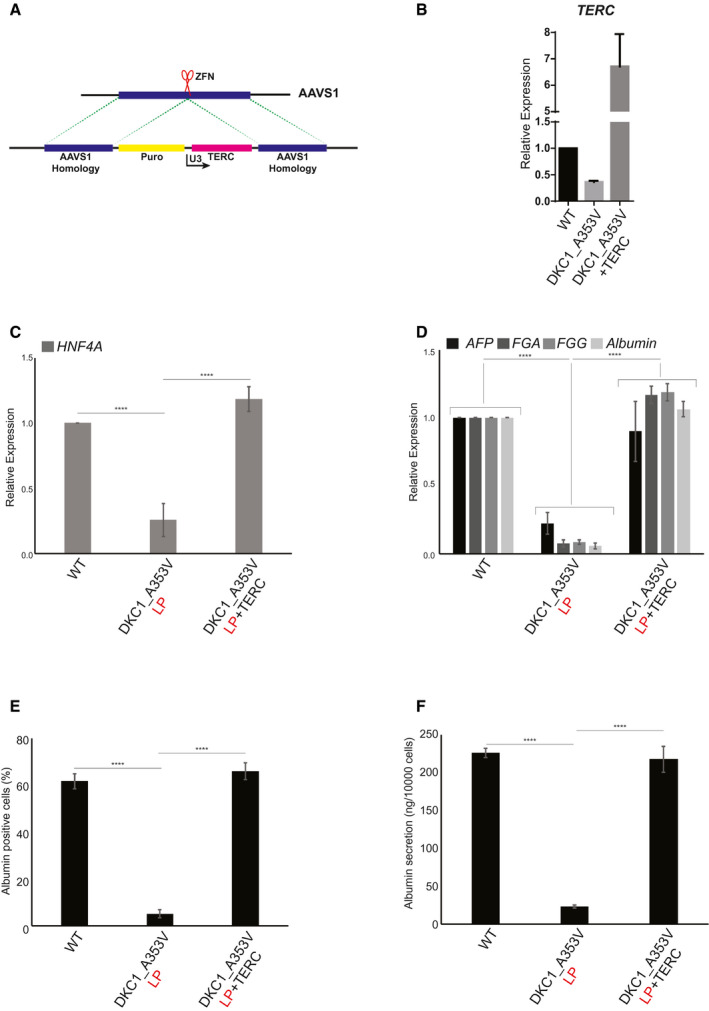
Reactivation of TERC rescues hepatocyte development from DKC1_A353V hESCs. (A) Model of AAVS1 targeting in DKC1_A353V hESCs. TERC is expressed under the control of a U3 promoter sequence in DKC1_A353V+TERC hESCs. (B) Quantification of TERC levels by real‐time quantitative PCR in WT, DKC1_A353V, and DKC1_A353V+TERC hESCs. (C) Quantification of HNF4α levels by quantitative RT‐PCR on day 11 of differentiation (hepatic endoderm stage) of WT, DKC1_A353V, and DKC1_A353V+TERC cells. (D) Relative expression of different hepatocyte markers (indicated in the figure) by real‐time quantitative PCR after 21 days of differentiation (mature hepatocyte stage) in WT, DKC1_A353V_LP, and DKC1_A353V+TERC cells. (E) Quantification of albumin‐positive cells by immunofluorescence after 21 days of differentiation in WT, DKC1_A353V_LP, and DKC1_A353V+TERC cells. (F) Quantification of albumin secretion by ELISA reading after 21 days of differentiation in WT, DKC1_A353V_LP, and DKC1_A353V+TERC cells. n = 3, mean ± SEM, ****P ≤ 0.0001. Statistical analysis was performed using one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
