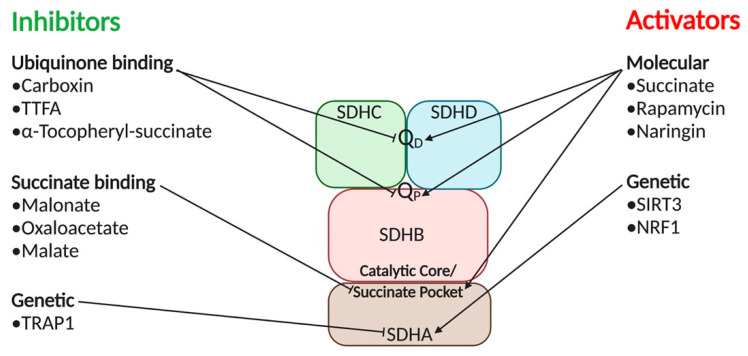
Figure 4.
Strategies for Targeting Succinate Dehydrogenase Complex. Ubiquinone binding inhibitors carboxin, TTFA, and α-Tocopheryl succinate bind and deactivate SDH at the proximal QP and distal QD ubiquinone binding sites. Ubiquinone binding inhibitors disrupt the reduction of ubiquinone to ubiquinol, a key step in the ETC. Succinate binding inhibitors malonate, oxaloacetate, and malate bind at the catalytic core or succinate pocket of SDH. Succinate pocket inhibitors are typically intermediates from the TCA cycle that modulate SDH activity based on cellular needs. Genetic inhibitor TRAP1 is a mitochondrial chaperone that inhibits SDH functions causing hypoxic environments that stimulate tumorigenesis. SDH activators such as succinate, Rapamycin, and Naringin function as small molecules activators of SDH. Additionally, genetic activator SIRT3 regulates the deacetylation of SDHA. NRF1 is an oxygen-sensing protein that binds to SDH genetic promoters when there is a lack of oxygen to limit ETC energy production until suitable oxygen conditions are resumed.