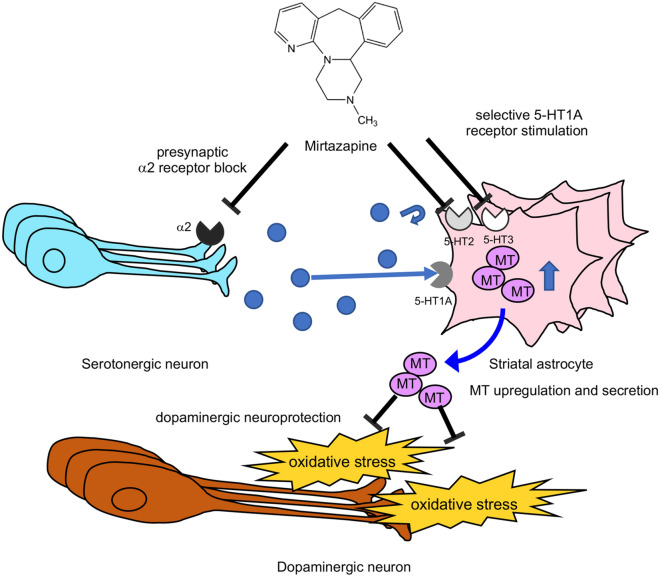
Figure. 8.
Schematic illustration of dopaminergic neuroprotective mechanisms of mirtazapine. Mirtazapine promotes the 5-HT release from serotonergic neuron by blocking adrenergic α2 receptors. Mirtazapine inhibits 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptor on astrocytes, which leads to selective 5-HT1A receptor stimulation and MT induction in astrocytes. MTs secreted from astrocytes attenuate oxidative stress and consequently protect dopaminergic neurons.