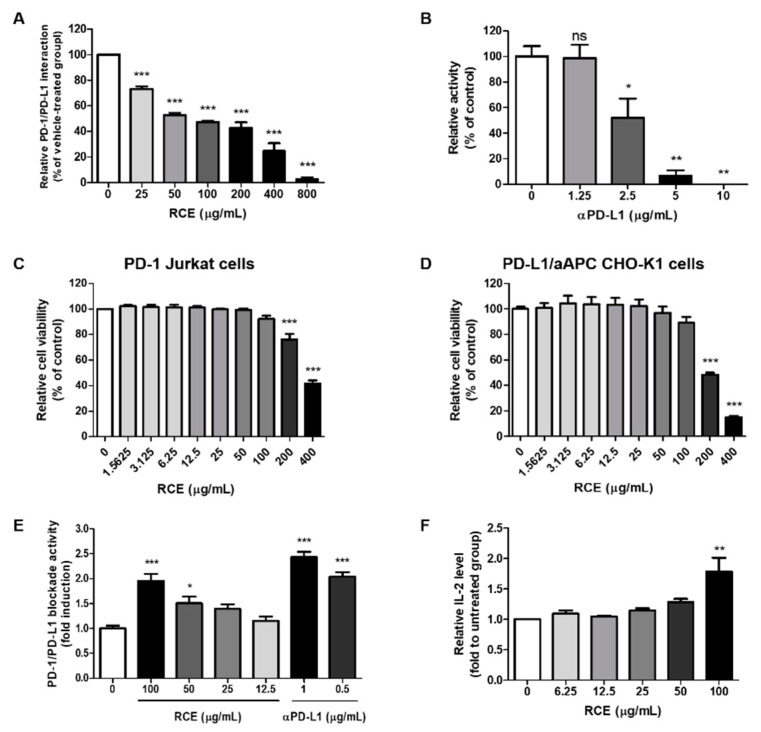
Figure 1.
Effect of Rubus coreanus extract (RCE) on programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/PD-1 ligand-1 (PD-L1) protein interaction using competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or cell-based assay. (A,B) The effect of RCE on the binding of PD-1 and PD-L1 in vitro using a competitive ELISA assay. (C,D) The effect of RCE on cell viability of PD-1/NFAT Jurkat cells (C) and PD-L1/aAPC CHO-K1 cells (E) using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK) assay. Each of the cells were treated according to the indicated concentrations of RCE for 24 h. (E) The effect of RCE on cellular PD-1/PD-L1 blockade activity. PD-1/NFAT Jurkat effector cells and PD-L1/aAPC CHO-K1 target cells were co-cultured with RCE or αPD-L1 for 24 h at the indicated concentrations. The relative PD-1/PD-L1 blockade activity were measured by PD-1/NFAT luciferase reporter assay. (F) Effect of RCE on IL-2 cytokine release in co-cultured cell model. Cell culture media was analyzed to measure IL-2 level by cytokine ELISA. Data are presented as mean ± S.E. of three representative independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant inhibition of PD-1/PD-L1 binding activity by each test inhibitor as compared with the vehicle-treated group; *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, compared with the vehicle group.