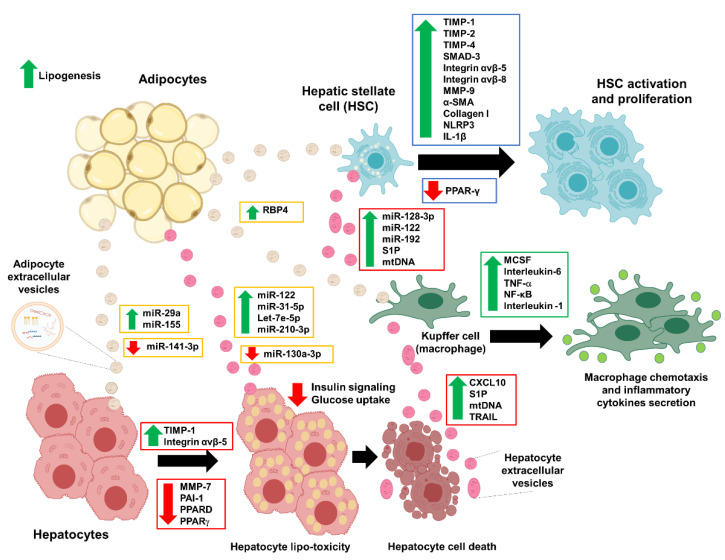
Figure 4.
Illustration of the extracellular vesicles’ involvement in NAFLD development. Adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles mediate the endocrine effects in hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells, and macrophages (Kuffer cells) in the early phase of the NAFLD development. The disease progression becomes worse when the hepatocytes release their extracellular vesicles that promote the formation of fibrosis. The green arrow represents upregulation, and the red arrow represents downregulation. Abbreviation: α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), C-X-C-motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10), interleukin-1 β (IL-1β), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF), matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPARD), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2), tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-4 (TIMP-4), TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α).