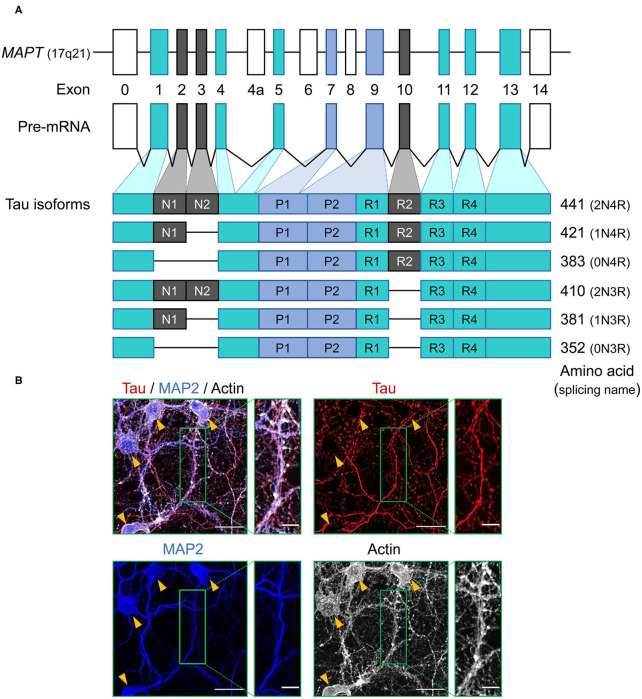
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of MAPT and the splice isoforms of tau in the human brain. (A) Human MAPT contains 16 exons. Exons in turquoise boxes (exons 1, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 12, 13) are constitutive, while the others are subject to alternative splicing. Exons 0 and 1 encode the 5′ untranslated sequences, and exon 14 is part of the 3′ untranslated region. Exon 4a, 6, and 8 are transcribed only in peripheral tissue, and alternative splicing of exon 2, 3, and 10 generates the six isoforms of tau. Tau isoforms translated from mRNAs that include exon 10, which encodes an additional microtubule-binding motif, are commonly referred to as four-repeat (4R) tau isoforms, whereas isoforms that exclude exon 10 are referred to as three-repeat (3R) tau isoforms. (B) Immunocytochemistry of tau (red) in primary hippocampal neurons at 21 days in vitro culture using anti-tau monoclonal antibody (RTM47 detecting 2-44 amino acid) with microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) counter stains in blue and actin stain with TRITC-labeled phalloidin in gray. Yellow arrowheads indicate neuronal soma. Scale bars, 30 μm and 10 μm in the boxed images. Image: L. Hromadkova.