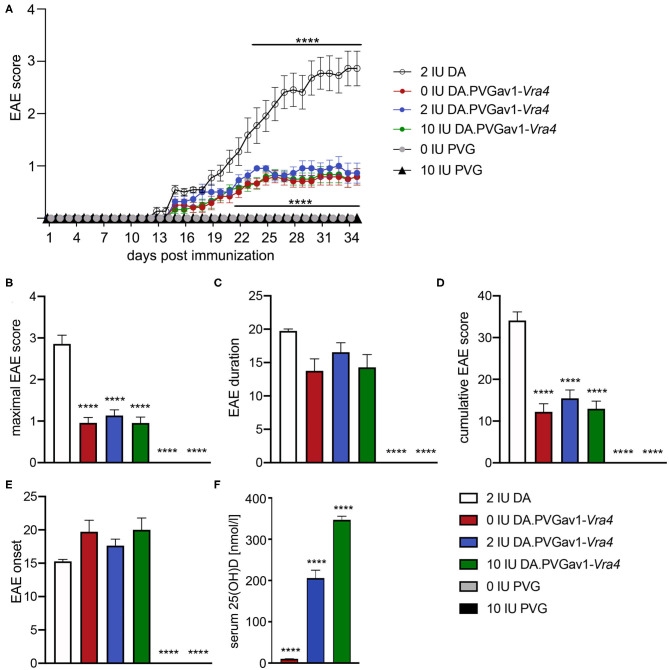
Figure 2.
Impact of vitamin D on the course of EAE in DA.PVGav1-Vra4 congenic and parental strains. (A) DA rats (n = 11) developed expectedly severe disease course, whereas PVG rats subjected either to vitamin D supplemented (n = 12) or deprived diet (n = 12) did not develop any signs of the disease. No additional modulation of essentially mild disease course in the congenic strain upon different concentrations of vitamin D (vitamin D supplemented (n = 12), vitamin D deprived (n = 12) and the regular diet group (n = 11)); both sexes included; data based on 2 pooled, independent experiments with comparable outcome. (B–E) Maximal EAE score, EAE duration, cumulative EAE score and EAE onset were comparable between the diet groups. (F) Serum levels of 25(OH)D were significantly different between the diet groups measured day 7 p.i. (n = 6 per diet group). Error bars represent SEM. Statistics were calculated using Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's correction for multiple testing (****p < 0.0001) for A and one-way ANOVA with Tukey correction for multiple testing (****p < 0.0001) for B-F. Statistical significances refer to comparison between DA.PVGav1-Vra4 and DA or DA.PVGav1-Vra4 and PVG, respectively.