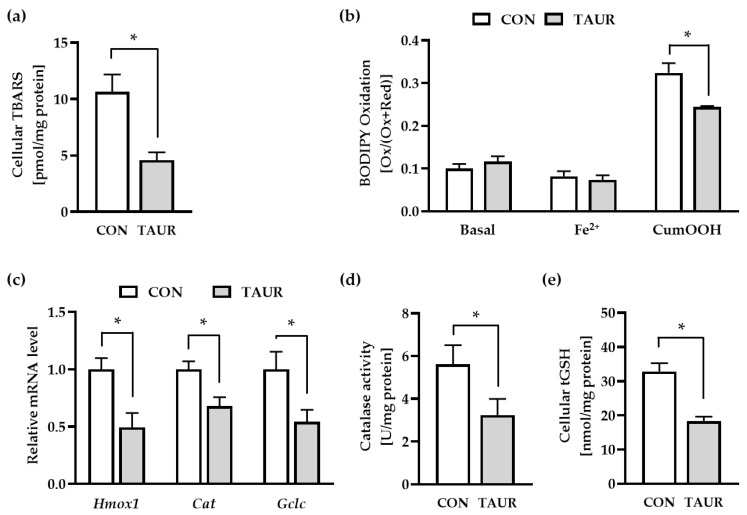
Figure 2.
Taurine (TAUR) reduced markers for lipid peroxidation (LPO) and cellular redox homeostasis. (a) TAUR reduced the level of secondary LPO products measured as thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS). (b) To examine LPO under basal and stress conditions, myotubes were treated with the fluorescent dye C11 (undecanoic acid)-BODIPY 581/591, and then DPBS buffer was added in the absence or presence of 2 µmol/L iron(II) sulfate (Fe2+) and 80 µmol/L cumene hydroperoxide (CumOOH). TAUR counteracted CumOOH-induced lipid peroxidation. BODIPY oxidation was determined by the ratio of oxidized to total BODIPY (oxidized + reduced) measured as fluorescence intensity. (c) The mRNA levels of heme oxygenase 1 (Hmox1), catalase (Cat) and glutamate-cysteine ligase, catalytic subunit (Gclc) were downregulated after 6 h of treatment with TAUR. (d) Catalase activity was significantly downregulated due to 24 h of incubation with TAUR compared to CON. (e) TAUR decreased the cellular content of total glutathione (tGSH = GSH + GSSG) under basal conditions. The data are shown as the means + SEM (n ≥ 6). * Indicates significant differences compared with CON; p < 0.05. Glutathione (GSH); glutathione disulfide (GSSG).