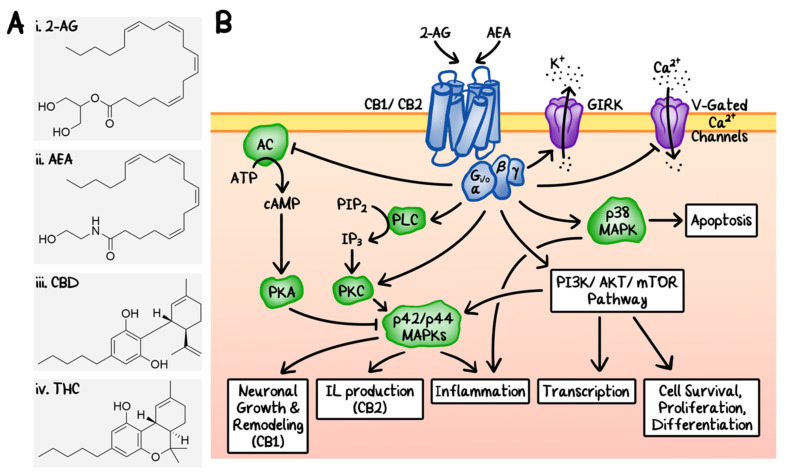
Figure 1.
Endocannabinoid system. (A) Chemical structures of two endogenous cannabinoids, 2-arachidonylglycerol (i, 2-AG) and N-arachidonylethanolamine (ii, AEA), and two representative exogenous cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa, cannabidiol (iii, CBD) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (iv, Δ9-THC). (B) Schematic diagrams of the signaling transduction pathways of the endocannabinoid system. 2-AG and AEA are agonists of CB1 and CB2. Some of the downstream effects include: (1) upregulation of p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) by direct inhibition of adenylyl cyclase (AC) and direct activation of phospholipase C (PLC), leading to the induction of neuronal growth, interleukin production, and inflammation. PKA: protein kinase A. PKC: protein kinase C. (2) Activation of p38 MAPK, which induces inflammation and apoptosis. (3) Activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways. Under certain conditions, these endocannabinoids can also induce transcription, cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation through similar pathways. Additionally, the cannabinoid receptors can also modulate ion channels including G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels (GIRKs) and voltage (V)-gated calcium channels.