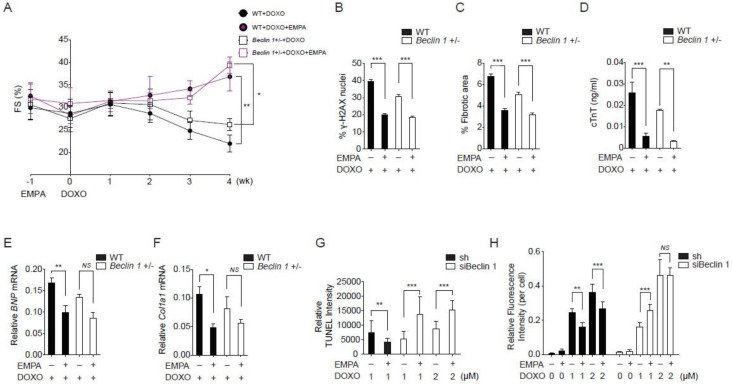
Figure 3.
Empagliflozin further protects doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in Beclin 1 deficient mice. (A) Left ventricular function determined by m-mode echocardiography at the indicated time points (n = 7 per group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, data were analyzed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey post hoc analysis). (B–F) Mice were sacrificed immediately following the fourth injection at week 4. (B) Phosphorylation of H2A histone family member X (γ-H2AX) staining of left ventricular sections, *** p < 0.001. (C) Picrosirius red staining, *** p < 0.001. (D) Serum cardiac troponin-T, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01. (E) BNP mRNA, ** p < 0.01, p = 0.06 for Beclin 1+/− + DOXO vs. Beclin 1+/− + DOXO/EMPA. (F) Col1a1 mRNA, * p < 0.05, NS, not significant (n = 7 per group, data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis). (G) TUNEL staining of the neonatal cardiomyocytes. (n = 4, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, data were analyzed by the Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA). (H) Cellular ROS detected by H2DCFDA fluorescence (n = 4, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, NS, not significant, data were analyzed by the two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis). Data are represented by mean ± s.e.m. (WT, wild-type; EMPA, empagliflozin; DOXO, doxorubicin; ROS, reactive oxygen species).