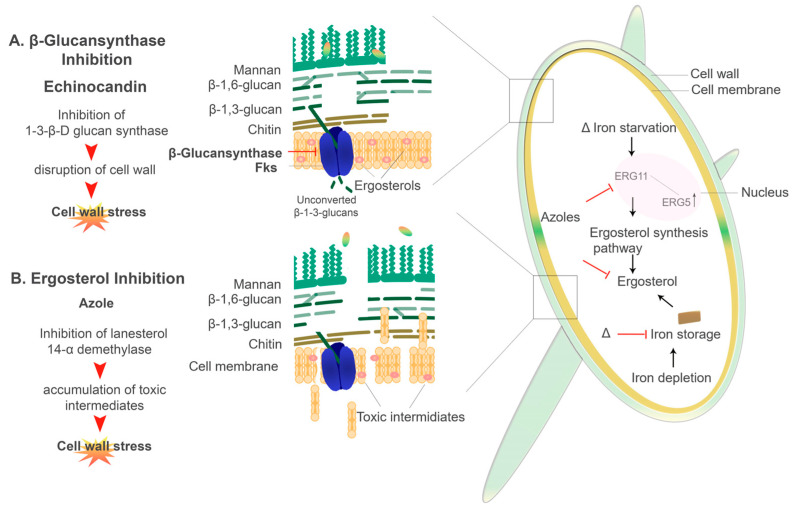
Figure 5.
Azoles and echinocandin antifungal drugs and their mechanism of actions: An illustration of two main classes of antifungal drugs used clinically and how they affect the fungal cell of C. albicans. (A) Echinocandins, e.g., caspofungin, inhibit β-(1-3)-D-glucan synthase in the cell membrane, which leads to disruption in cell wall integrity. (B) Azoles, e.g., fluconazole, inhibit Erg11/CYP51 F5, which blocks the production of ergosterol, leading to the accumulation of toxic sterol intermediates. Δ indicates where iron starvation or depletion may contribute to increased susceptibility to azole antifungals.