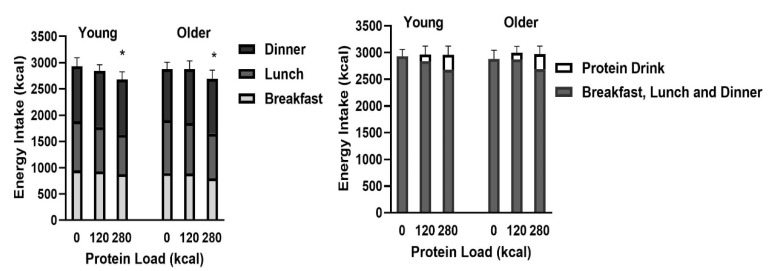
Figure 1.
Energy intake at breakfast, lunch, and dinner following whey protein ingestion in healthy young and older men. Mean (± SEM) ad libitum energy intake (kcal; left) at breakfast (light grey bars), lunch (dark grey bars), and dinner (black bars) following drink ingestion containing flavored water (control, ~2 kcal) or whey protein (30 g/120 kcal or 70 g/280 kcal) and cumulative energy intake (kcal; right; sum total energy intake at breakfast, lunch, and dinner combined (dark grey bars) and protein drink (white bars)) in young (left; n = 15) and older (right; n = 15) men. Age and protein load main effects and interaction effects were determined by repeated measures ANOVA. * The 70 g protein drink suppressed energy intake (sum of breakfast, lunch, and dinner) compared with the control (protein load effect P = 0.012, post-hoc P = 0.023).