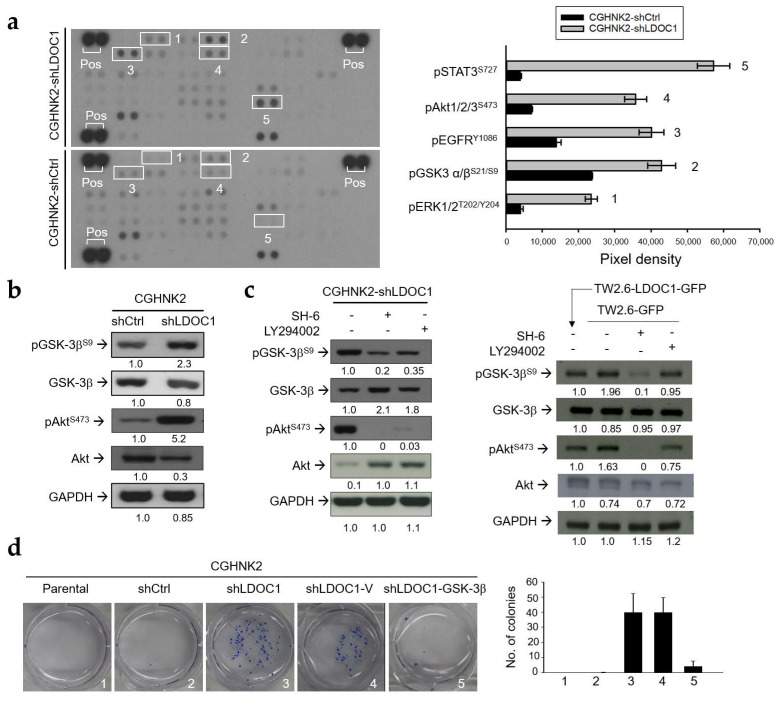
Figure 5.
LDOC1 downregulation leads to inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3βS9 by pAktS473 and GSK-3β regulates the clonogenicity of the CGHNK2-shLDOC1 cell line. (a) Results of the human phosphokinase array analysis using CGHNK2-shLDOC1 and CGHNK2-shCtrl cells. The bar charts represent the relative protein phosphorylation levels for the top four kinases and the transcription factor STAT3 exhibiting different phosphorylation states in CGHNK2-shLDOC1 and CGHNK2-shCtrl cells (the array contained some non-kinase phosphoprotein spots). Experiments were performed according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer, as described in Materials and Methods. (b) Western blotting analysis of pGSK-3βS9, GSK-3β, pAktS473, and Akt in CGHNK2-shLDOC1 and CGHNK2-shCtrl cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control for each protein sample. (c) The serine kinase activity of Akt is required for the phosphorylation of GSK-3βS9 in CGHNK2-shLDOC1 and TW2.6-GFP cells. Cellular protein lysate was harvested after a 6 h treatment with inhibitors of Akt (SH-6, 5 μM) or PI3K (LY294002, 10 μM). Western blotting analyses of pGSK-3βS9, GSK-3β, pAktS473, Akt, and GAPDH were then performed. Cells treated with PBS (0.1%) were used as controls. The pixel intensity ratio for each band was shown. There are technical duplicates for the human phosphokinase array analysis; Western blotting analysis under each condition was performed at least twice. (d) Ectopic expression of GSK-3β inhibits the acquired clonogenicity of CGHNK2-shLDOC1 cells. Cells were subjected to a colony-forming assay. The bar chart represents the mean values of triplicate tests (mean ± SD). Representative images are presented.