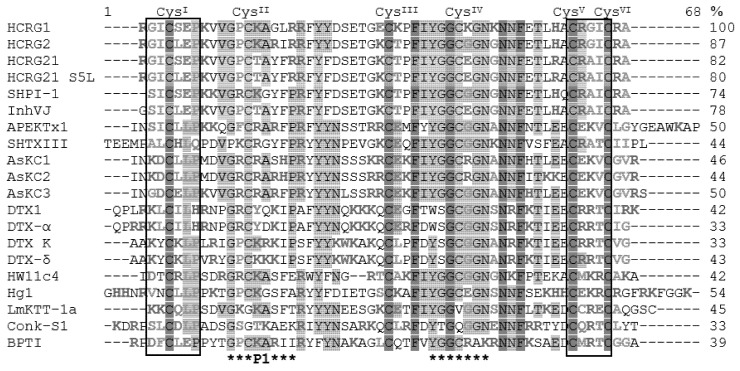
Figure 4.
Multiple alignment of Kunitz peptides, blockers of Kv channels and BPTI. APEKTx1 (P61541) from the sea anemone A. elegantissima, AsKC1–AsKC3 (Q9TWG0, Q9TWF9, Q9TWF8) from A. sulcata, ShPI-1 (P31713) from S. helianthus, SHTXIII (B1B5I8) from S. haddoni, HCRG1, HCRG2, HCRG21, HCRG21 S5L, and InhVJ from H. crispa, HW11c4 (A0A023WBH6) from spider Ornithoctonus huwena; LmKTT-1a (P0DJ46) from scorpion Lychas mucronatus, Hg1 (P0C8W3) from Hadrurus gertschi; DTX1 (P00979), DTX-K (P00981) from snake Dendroaspis polylepis, DTX-α (P00980), DTX-δ (P00982) from Dendroaspis angusticeps; Conk-S1 (P0C1X2) from cone snail Conus striatus; BPTI (P00974) from bovine Bos taurus. Identical amino acids are shownondark-grey and conservative on light-gray background. Hydrophobic amino acids are indicated by green, positively charged by blue, negatively charged by red, and polar non-charged by pink letters. Frames highlight regions responsible for interaction with Kv channels [19]. Asterisks indicate a reactive site with P1 residue and site of weak interaction with serine proteases.